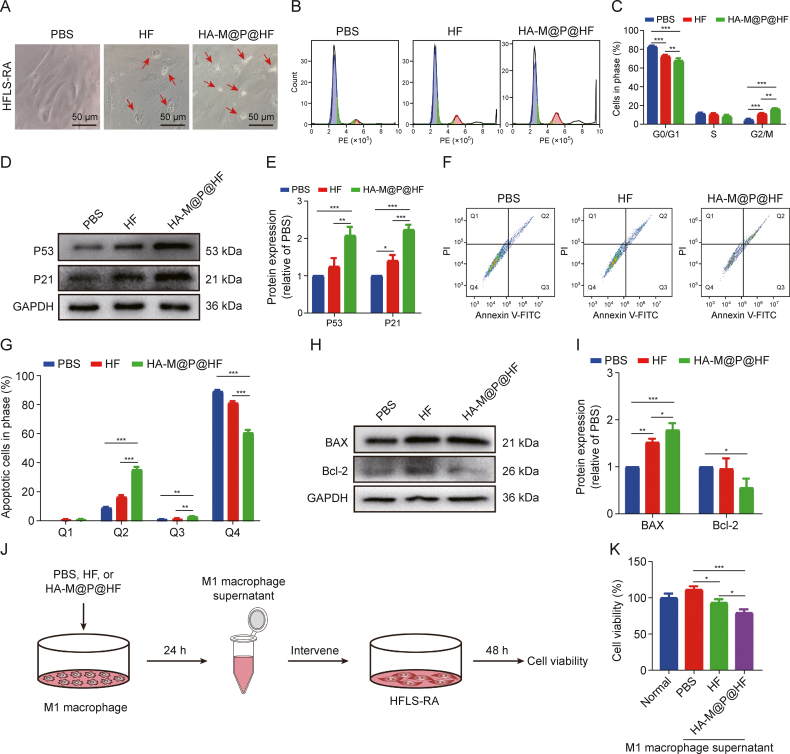
Fig. 5.
In vitro anti-arthritic effects and mechanism of hyaluronic acid (HA)-modified hybrid membrane (M)-camouflaged poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) loaded halofuginone hydrobromide (HF) nanoparticles (NPs) (HA-M@P@HF NPs). (A) Morphological images of human fibroblast-like synoviocytes-rheumatoid arthritis (HFLS-RA) with different treatments for 48 h. The red arrows indicate apoptotic cells. (B, C) Flow cytometry images (B) and quantitative analysis (C) of cell cycle assay of HFLS-RA with different treatments by flow cytometry. (D, E) Western blotting assay (D) and quantitative analysis (E) of P53 and P21 levels with different treatments. (F, G) Apoptosis detection (F) and quantitation (G) after various treatments by flow cytometry. Q1−Q4 indicate necrosis rate, late apoptosis rate, early apoptosis rate, and non-apoptotic rate, respectively. (H, I) Western blot images (H) and quantitative analysis (I) of Bcl-2-associated X protein (BAX) and Bcl-2 levels with different treatments. (J) Intervention process of M1 macrophage inflammatory supernatant on HFLS-RA. (K) The effect of M1 macrophage inflammatory environment on the cell viability of HFLS-RA. Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) was used as the negative control. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. PE: phycoerythrin; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PI: propidium iodide; FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate.