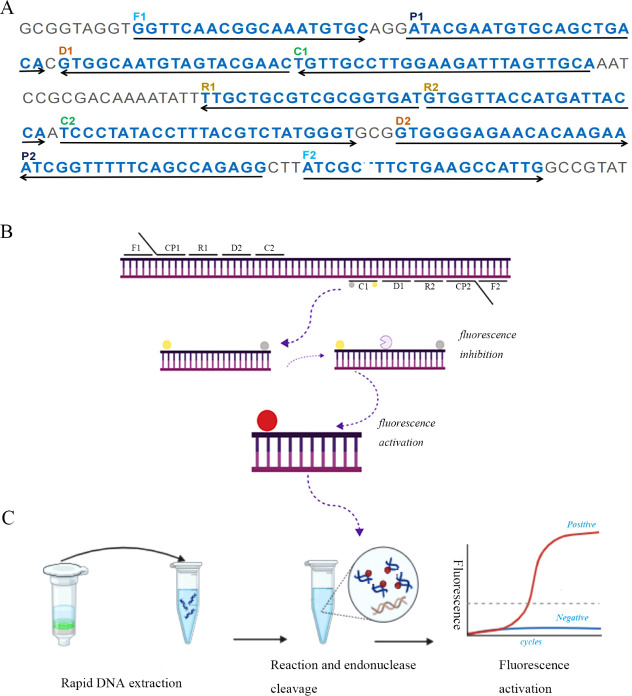
Figure 1.
Diagrammatic representation of the NM-RT-MCDA assay’s foundation. (A) The study’s primers’ locations and sequences that target the N. meningitis ctrA gene. Sense and complementary sequences are indicated by the right and left arrows, respectively. The primer positions are indicated by the yellow colored text. There are six amplification primers (C1, C2, D1, D2, R1 and R2), two cross primers (CP1 and CP2), and two displacement primers (F1 and F2). (B) MCDA reactions schematic diagram using the modified primers. A quencher (BHQ1, gray ball) was inserted in the middle of primer C1, which was extended with an endonuclease recognition site at the 5′ end and a fluorophore (FAM, yellow ball) at the 5′ end. Double-stranded target amplification containing the restriction endonuclease recognition site were produced following amplification. The fluorescent signal was produced upon recognition and cleavage by restriction endonuclease. (C) The NM-RT-MCDA detection system in its entire form. The entire procedure, which includes real-time fluorescence detection, MCDA reaction, endonuclease cleavage, and real-time DNA extraction.