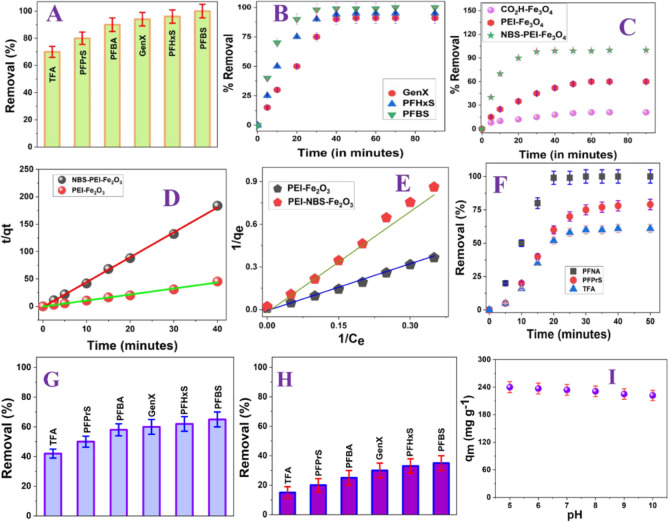
Figure 3.
(A) Removal efficiency for short- and ultrashort-chain PFAS (1 μg/L) from drinking water using the NFBS and PEI-attached magnetic nanoadsorbent (1 mg/L). (B) Plot showing the time-dependent removal efficiency for short-chain PFAS using the nanoadsorbent. (C) Plot showing the time-dependent removal efficiency for short-chain PFBS from drinking water using different nanoadsorbents. (D) Plot showing how t/qt varies with time for PFBS removal from drinking water. (E) Plot showing how 1/qe varies with 1/Ce for PFBS removal from drinking water. (F) Plot showing the time-dependent removal efficiency for PFNA, PFPrS, and NFA using the nanoadsorbent. (G) Removal efficiency for short- and ultrashort-chain PFAS (1 μg/L) from drinking water using the PEI-attached magnetic nanoadsorbent (1 mg/L). (H) Removal efficiency for short- and ultrashort-chain PFAS (1 μg/L) from drinking water using the carboxy-attached magnetic nanoadsorbent (1 mg/L). (I) Plot showing pH-dependent PFBS removal efficiency using the nanoadsorbent.