FIGURE 4.
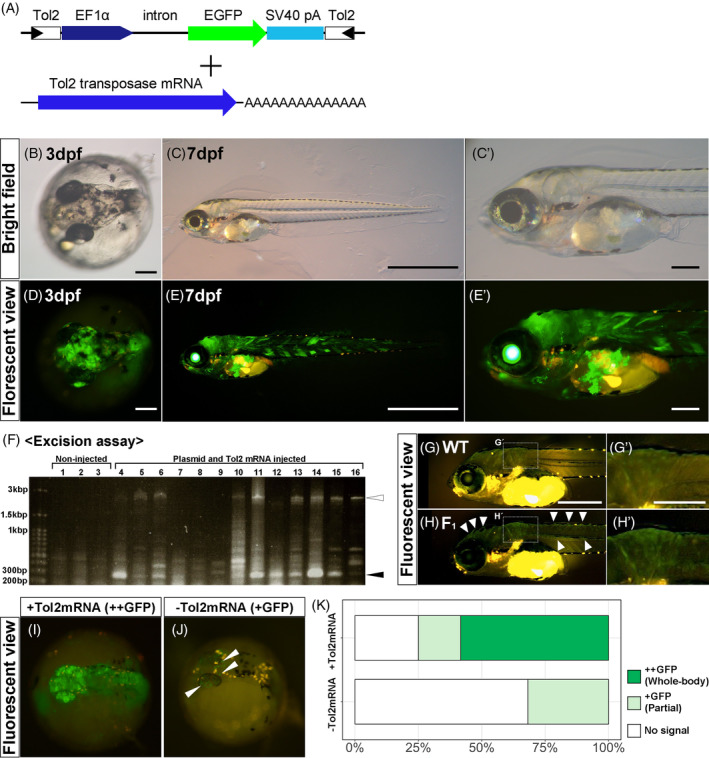
(A) Injected DNA and mRNA constructs. The Tol2 construct (pT2AL200R150G) was co‐injected with Tol2 transposase mRNA. (B)–(E’) GFP expression in embryos injected with the Tol2 constructs at two different developmental stages: 3 days post‐fertilization (dpf) (B), (D) and 7 dpf (C), (C’), (E), (E’). Both bright field (top) and fluorescent (bottom) images are shown. For the 7 dpf fish, magnified views are also shown (C’), (E'). (F) An electrophoresis gel image of PCR products for Tol2 excision assay. A black arrowhead indicates the position of bands of PCR amplicons from the Tol2 excised construct. A white arrowhead indicates the position of bands from the intact construct. (G)–(H’) Comparing the GFP expression between wildtype and F1 embryo at 6 dpf. White arrowheads and bracket indicate GFP‐positive signals. (I)–(K) Functional validation of the Tol2 transposase mRNA in terms of transgenesis efficiency. (I), (J) Representative images of GFP expression in 2 dpf embryo injected with (I) or without (J) Tol2 transposase mRNA. Ubiquitous GFP expression (GFP++) was observed in the embryo co‐injected with both the Tol2 construct and the mRNA (I), while partial GFP expression (GFP+) was shown in the embryo injected only with the DNA construct (J). White arrowheads indicate GFP‐positive signals. (K) Efficiency of GFP expression with or without Tol2 transposase mRNA. Scale bars indicate 200 μm (B), (D), (C’), (E’), (G’), 500 μm (G) or 1 mm (C), (E).
