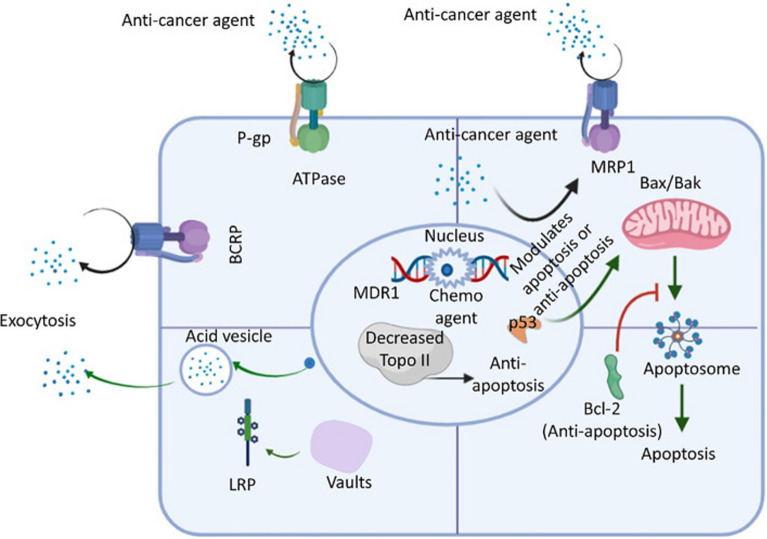
Fig. 5.
An review of the ABC transporter, LRP, Bcl-2, and Topo ll drug resistance pathways in cancer cells. An ATP-activated transporter is the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter. To remove foreign molecules (such as antibiotics and anticancer drugs) from the intracellular environment, cells express ABC transporters during general chemotherapy. The three main members of the ABC transporter family are P-glycoprotein (P-gp), multidrug-resistant protein 1 (MRP-1), and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). Lung resistance protein (LRP) is found in cytoplasmic vaults and aids in the exocytosis of foreign substances, such as anticancer medications. Additionally, studies have shown that p53 loss of function, downregulation of topoisomerase II (Topo-II), and upregulation of bcl-2 (an antiapoptotic factor acted upon by anticancer agents that activate the normal apoptotic process) also decrease cell apoptosis to increase the resistance of cancer cells to anticancer drugs [353, 354]