Fig. 4.
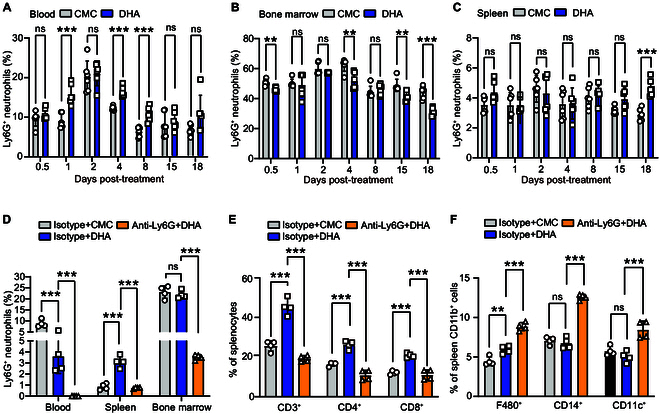
DHA regulates the host immune response through Ly6G+ neutrophils. (A) A significant increase in Ly6G+ neutrophils was observed in the peripheral blood of mice on days 1, 4, and 8 after treatment with DHA (n = 6, P = 0.0007, P = 0.0001, and P = 0.0008). (B) Ly6G+ neutrophils in the bone marrow decreased significantly after DHA treatment on days 1 (P = 0.0029), 4 (P = 0.0030), 15 (P = 0.0029), and 18 (P = 0.0002) (n = 6). (C) Ly6G+ neutrophils in the spleen increased significantly after DHA treatment on day 18 (n = 6, P = 0.0004). (D) Ly6G+ neutrophils in the peripheral blood, bone marrow, and spleen of the mice injected with anti-Ly6G mAb and DHA decreased significantly compared to those treated with an isotype mAb and DHA (n = 4, P < 0.0001). (E) CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells in the spleen decreased significantly in the anti-Ly6G mAb group compared with the isotype group (n = 4, P < 0.0001). (F) F4/80+ CD11b+, CD14+CD11b+, and CD11c+ CD11b+ cells in the spleen increased significantly in the anti-Ly6G mAb group compared with the isotype group (n = 4, P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001, and P = 0.0005). ns: P > 0.05; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
