FIGURE 1.
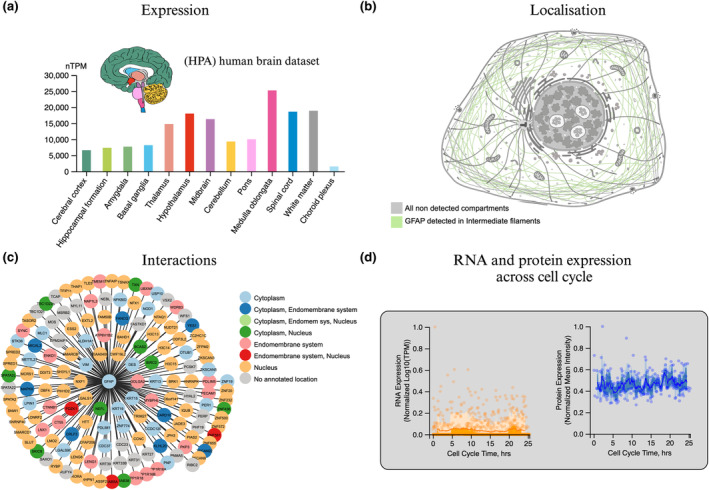
Biology of GFAP curated by Human Protein Atlas (HPA). GFAP is a highly dynamic structural protein involved in a plethora of biological processes, including but not limited to maintaining the integrity of the blood–brain barrier (BBB; Liedtke et al., 1996). (a) Brain‐specific expression of GFAP based on RNA consensus dataset consists of normalised expression levels of 13 brain regions (Uhlén et al., 2015). (b) GFAP localisation characterised by presence in all tested cells (Thul et al., 2017). (c) Interaction summary network of GFAP. The thickness of the edges represents the confidence of the interaction and nodes are coloured according to subcellular location. (d) GFAP RNA and protein expression are highly regulated during the cell cycle as GFAP is essential for the remodelling of glial frameworks in mitosis (Kawajiri et al., 2003; Messing et al., 1998; Rutka et al., 1994; Yoshida et al., 2007). The RNA expression level was determined by single‐cell RNA sequencing of the U‐2 OS FUCCI cell line. This cell line is a variant of the human cervical carcinoma cell line HeLa. Protein expression was determined by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy in the U‐2 OS FUCCI cell line. Normalised RNA and protein expression in individual cells is plotted along a linear representation of cell cycle pseudotime, as determined from the fluorescence intensities of the cell cycle markers (Karlsson et al., 2021).
