FIGURE 3.
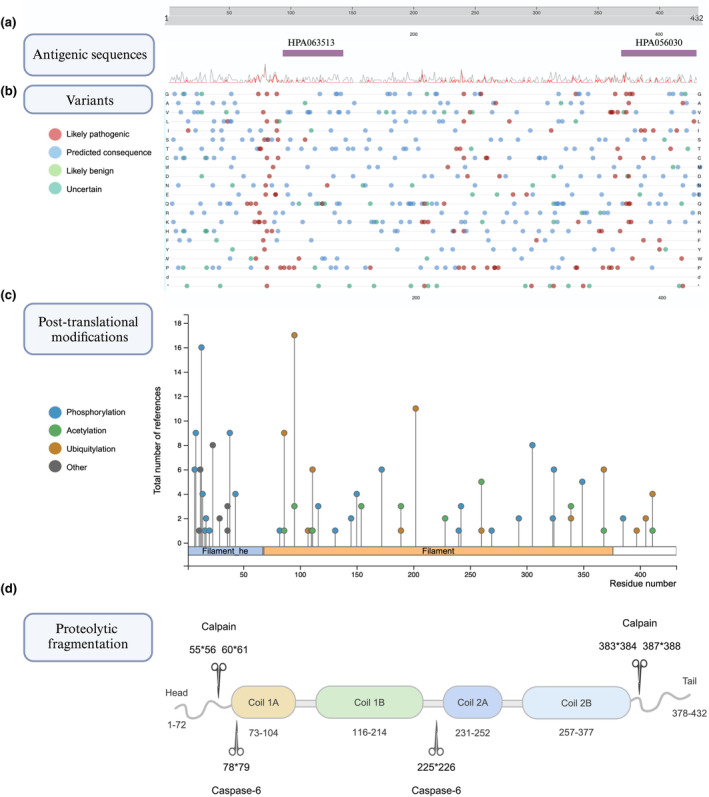
GFAP feature overview and breakdown products. GFAP and its modified or cleaved products play a key role in various cellular processes. GFAP epitopes which are targeted by commercially available immunoassays are mostly poorly characterised. (a) Demonstrates known antigenic sequences along the full‐length GFAP (antibodies targeting GFAP: HPA063513; HPA056030) and (b) mutations curated by UniProt (Consortium, T. U, 2023). Mutations and types of modifications are colour‐coded. (c) Protein post‐translational modifications (PTMs) functionally regulate the localisation, activity and assembly of GFAP. The visualisation of PTMs is based on PhosphoSitePlus (Hornbeck et al., 2014). (d) Full‐length GFAP is susceptible to proteolysis by calpain and caspase enzymes. A schematic representation of the proteolytic fragmentation of GFAP is shown. GFAP is shown as a linear model and major calpain and caspase 6 cleavage sites are indicated with scissors, whereby asterisks show between which amino acids the cleavage sites are. Adapted from Yang et al. (2022).
