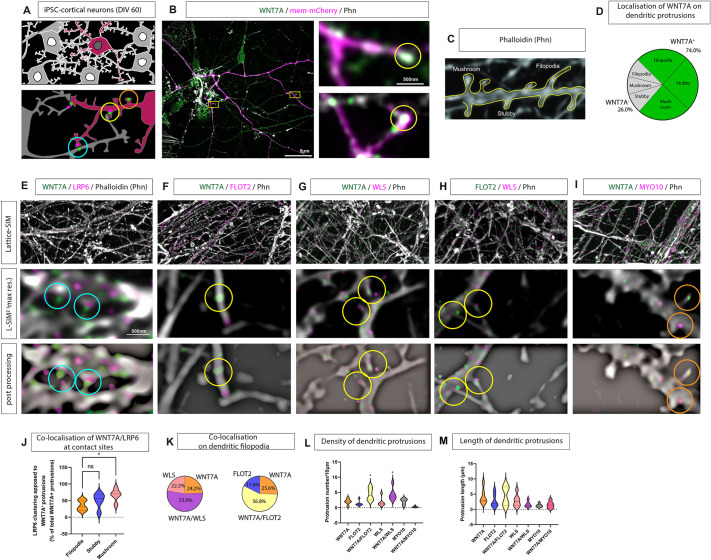
Fig. 1.
Characterisation of dendritic filopodia as WNT7A-carrying signalling filopodia. (A) Schematic of iPSC-derived cortical neuron cultures at 60 days in vitro (DIV 60), transfected with membrane marker and co-stained with antibodies to observe localisation of WNT7A, LRP6, and classical filopodia/cytoneme markers. Blue circles denote areas of opposing localisation of proteins across membranes, yellow circles denote proper protein colocalisation, and orange circles no colocalisation. (B) Super-resolution imaging of iPSC-derived cortical neurons stained with anti-WNT7A antibody shows localisation of the protein to dendritic protrusions. Boxed areas are shown at higher magnification on the right. (C,D) Quantification (D) of dendritic protrusion types (filopodia, stubby, mushroom; C) found that nearly 75% of total protrusions were WNT7A positive with no difference in the distribution of WNT7A protein across the class of protrusion. (E) Super-resolution microscopy of neurons co-stained with antibodies against WNT7A and LRP6 shows localisation of WNT7A on dendritic protrusions, whereas LRP6 generally localises at opposing membranes (E, blue circles). WNT7A-positive protrusions also harbour proteins associated with Wnt-signalling filopodia, such as flotillin 2 (FLOT2; F, yellow circles) and Wntless/evenness interrupted (WLS; G, yellow circles), with over 50% of WNT7A-positive protrusions colocalising with these cytoneme markers. Conversely, the Wnt-signalling filopodia marker Myo-10 localises to a WNT7A-negative subset of protrusions (I, orange circles). FLOT2 and WLS colocalise on the same protrusions (H, yellow circles). (J) Quantification of LRP6 and WNT7A co-clustering at apposing membranes identified a significant increase in co-clustering of WNT7A-positive mushroom-shaped protrusions and LRP6 compared to co-clustering at filopodia contacts. (K) Quantification of protrusion number based on cytoneme markers found significantly more WNT7A/FLOT2-positive and WNT7A/WLS-positive protrusions compared to WNT7A-only positive protrusions, and 74% of all protrusion analysed were WNT7A positive. (L,M) Quantification of protrusion density (L) and length (M) found no difference based on the colocalisation of WNT7A with cytoneme protein markers. Statistical significance was addressed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test to compare relevant controls within groups. *P<0.05. ns, not significant.