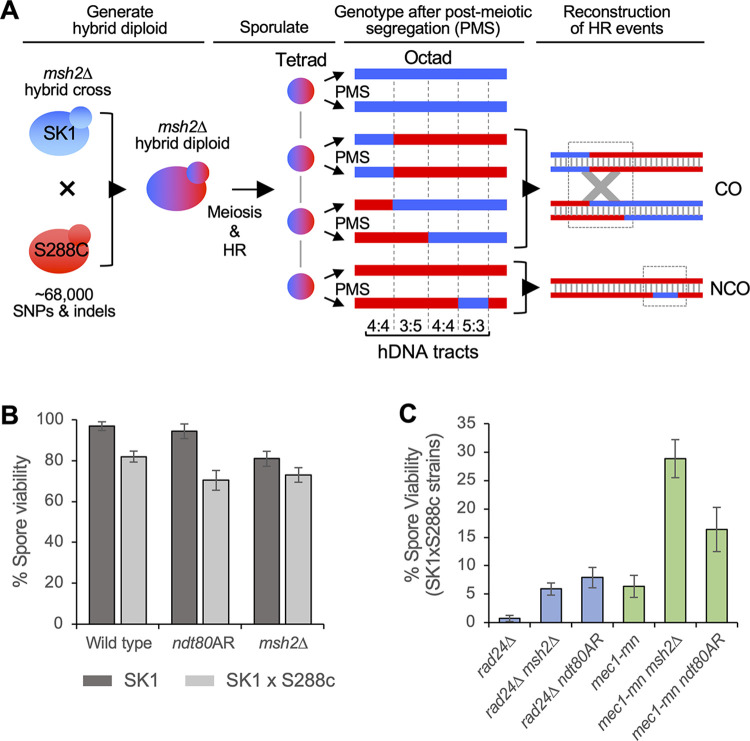
Fig 1. Overview of recombination analysis strategies.
A) Strategy for whole-genome mapping of HR events in octads after post-meiotic segregation (PMS) of hDNA. For simplicity, a single chromosome is shown containing one CO and one NCO. Haploid cells from the S288c (red) and SK1 (blue) genetic backgrounds are crossed, producing a hybrid diploid containing many polymorphisms. The diploid undergoes meiotic recombination, forming CO and NCO events with associated hDNA tracts. These are left unrepaired in strains with a deletion of the mismatch repair protein Msh2, but are converted or restored in MSH2 strains. At the conclusion of meiosis, the four chromatids are distributed among four ascospores. To preserve hDNA information, each spore is allowed to undergo one mitotic division, after which the mother and daughter cells are separated to produce eight haploid cell lines, the genomes of which are equivalent to the eight DNA strands involved in the meiotic recombination event. The eight genomes are sequenced to retrieve polymorphism information at each position, allowing precise hDNA reconstruction genome-wide. B,C) Spore viability is severely reduced in rad24Δ and mec1-mn, which is prohibitive to their analysis. To enable sequencing of all four meiotic products, spore viability is increased by prophase extension (8 hours) or MSH2 deletion. Spore viability comparison for the indicated strains and non/hybrid backgrounds. Error bars indicate 95% confidence limits.