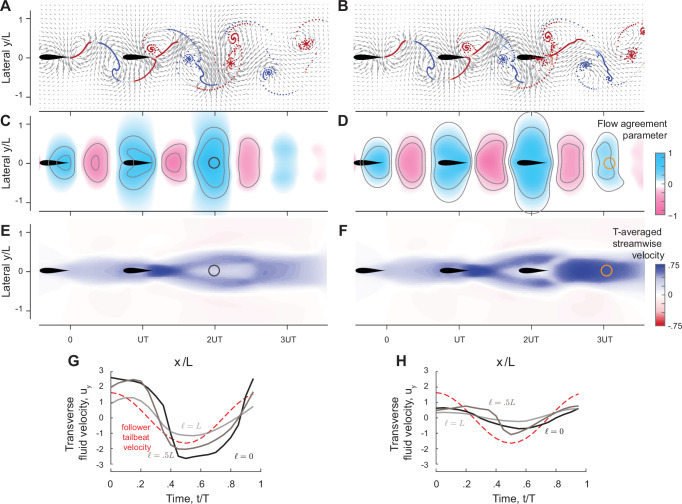
Figure 9. Prediction of equilibrium locations in the wake of multiple upstream swimmers.
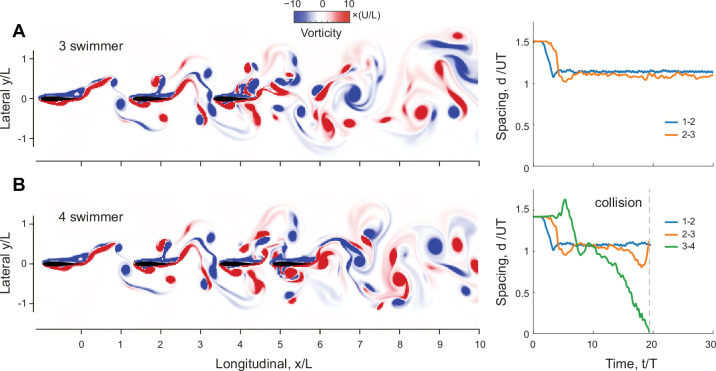
(A, B) Snapshots of vorticity fields created by two inline inphase swimmers, and three inline inphase swimmers. (C, D) show the corresponding flow agreement parameter fields. Contour lines represent flow agreement parameter at ±0.25, ±0.5. (E, F) plot the corresponding period-averaged streamwise velocity. Separation distances predicted by the locations of maximal are marked by circles in the flow agreement field. In the left column, separation distances based on freely swimming triplets are marked by black circles and coincide with the locations of maximal . In the right column, the orange marker shows the prediction of the location of a fourth swimmer based on the maximum flow agreement parameter. In two-way coupled simulation, swimmer 4 actually separates from the leading three swimmers as illustrated in Figure 8A. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation shows swimmer 4 will collide with swimmer 3 as in Figure 9—figure supplement 1. (G, H) show the transverse flow velocity in a period at the location predicted by the maximum flow agreement parameter and with a lateral offset , in comparison to the follower’s tailbeat velocity.