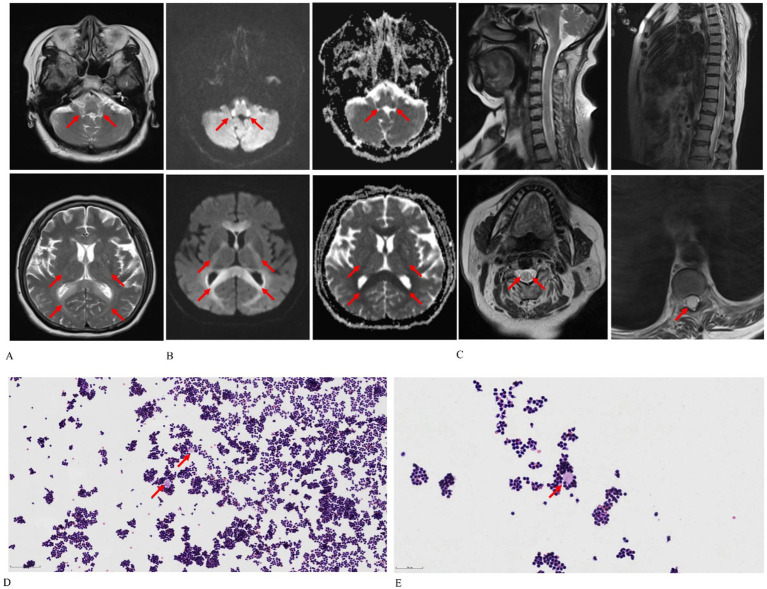
Figure 1.
Chlorfenapyr and emamectin benzoate-induced leukoencephalomyelopathy in a 65-year-old female patient. (A) Axial T2-weighted images reveal diffuse and bilaterally symmetrical leukoencephalopathy affecting the dentate nucleus of the cerebellum, ventral medulla, bilateral inferior cerebellar peduncles, pons, midbrain, bilateral cerebral peduncles, bilateral corticospinal tracts, corpus callosum, and bilateral parieto-occipital white matter. (B) Axial diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient maps demonstrate cytotoxic edema and reduced Brownian motion. (C) Sagittal T2-weighted spine images display swelling and hyperintensity throughout the spinal cord, particularly in the cervical region and conus medullaris. (D,E) Cytological smears of cerebrospinal fluid [optical microscope: Hematoxylin–eosin stain, 100× (D), 200× (E)] show lymphocytes clustering around protein-like material in a wreath-like formation, as indicated by the red arrow.