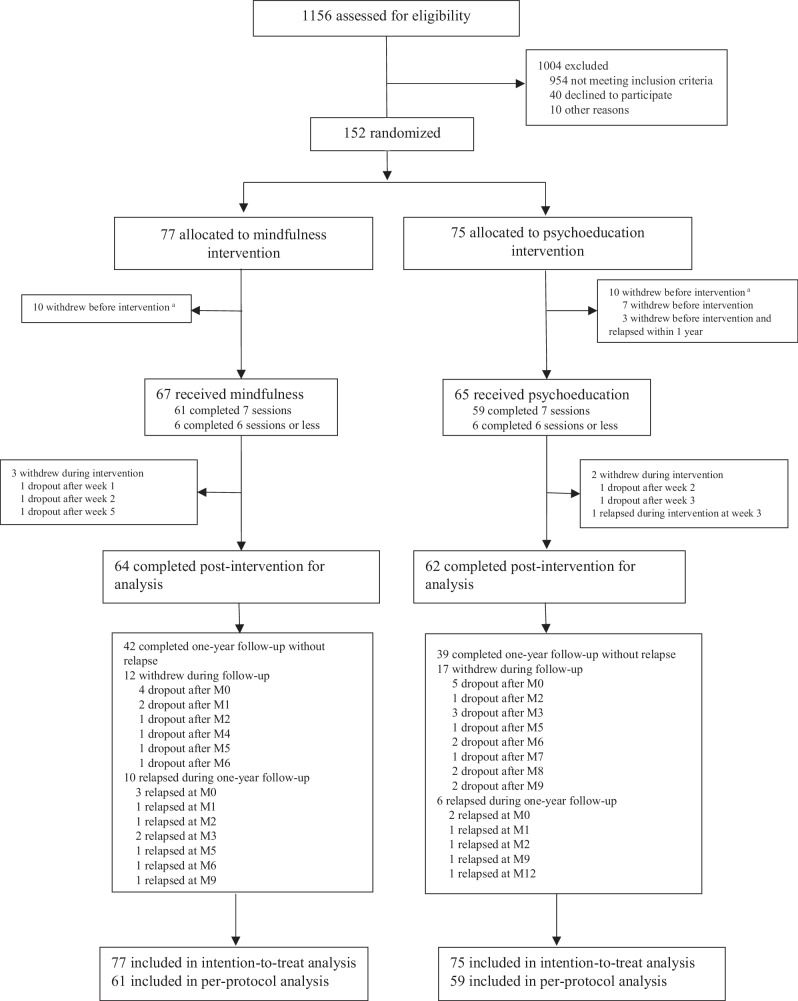
Fig. 1.
Enrollment and outcomes. aThe relapse status of patients who dropped out before the intervention (n = 20) was assessed using the Clinical Management System (CMS). Relapse was defined as the deterioration of symptoms meeting the relapse criteria within one year of their baseline assessment date, as documented in their CMS case notes. For the rest of the patients (n = 132), relapse status was assessed from monthly assessment based on the deterioration of symptoms meeting the relapse criteria. The relapse criteria was the presence of all the following conditions for at least one week: (1) an increase in at least one of the following PANSS27 items (delusion, hallucinatory behavior) to a score of ≥3; (conceptual disorganization, unusual thought content) to a score of ≥4; (suspiciousness) to a score of ≥5; (2) Clinical Global Impression (CGI) Severity of Illness29 scale rated ≥3; and (3) CGI Improvement scale rated ≥5. Continuous variables were also created for individual relapse item scores (e.g., PANSS delusion).