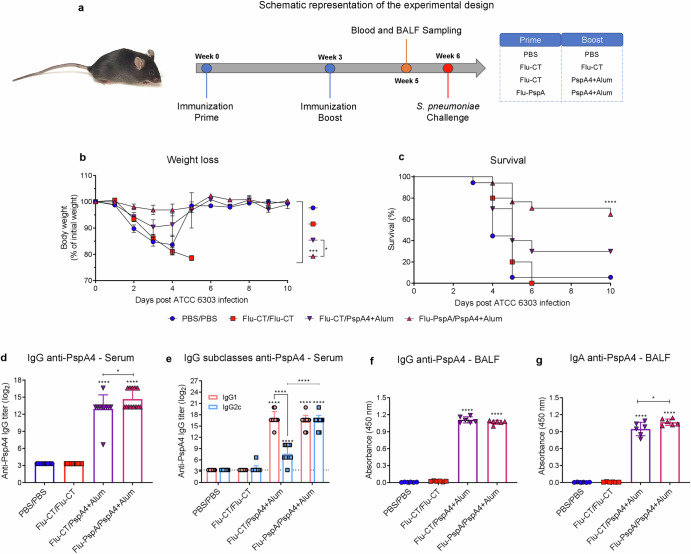
Fig. 5. Optimization of the heterologous prime-boost protocol with Alum adjuvant.
a Schematic design to evaluate the efficacy of the optimized heterologous prime-boost protocol, b weight loss, c survival mice after lethal challenge with pneumococcus (ATCC 6303), d reactivity of IgG, e IgG subclasses for the PspA4 protein in the serum, f reactivity IgG and (g) IgA antibodies specific for the PspA4 protein in BALF. PBS/PBS: animals that received two doses of PBS; Flu-CT/Flu-CT: animals that received two doses of 105 PFU of control recombinant virus; Flu-CT/PspA4+Alum: animals that received 105 PFU of control recombinant virus and boosted with 5 µg of PspA4 adjuvanted with alum; Flu-PspA/PspA4+Alum: animals that received 105PFU of Flu-PspA recombinant virus and boosted with 5 µg of PspA4 protein adjuvanted with alum, all immunization intranasally. Serum and BALF were collected 14 days after the boost, and serum antibody titers were represented as the log2 of the reciprocal of the highest dilution at which the O.D. at 450 nm presenting a value ≥0.1. For BALF analyses, quantification was represented by the O.D. value at 450 nm using the pure sample. The bars represent the means ± standard deviation of three independent experiments (b–e) or one experiment (f and g), with at least 5 animals per group. Differences between were determined by ANOVA (p < 0.05). *, **, ***, and **** indicate significant differences at p values <0.05, <0.01, <0.001, and <0.0001, respectively. The survival curves were compared using the Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) and Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon tests. The differences between the weight loss curves were calculated from the area under the curve.