Abstract
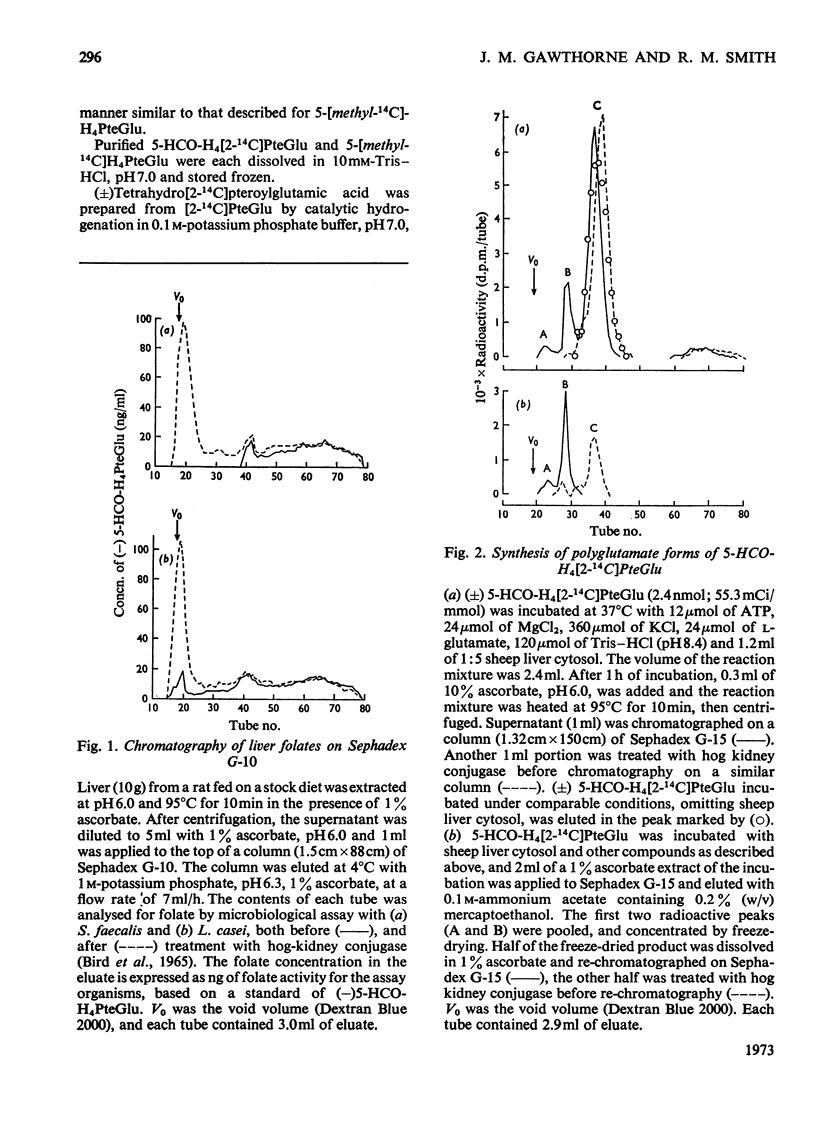
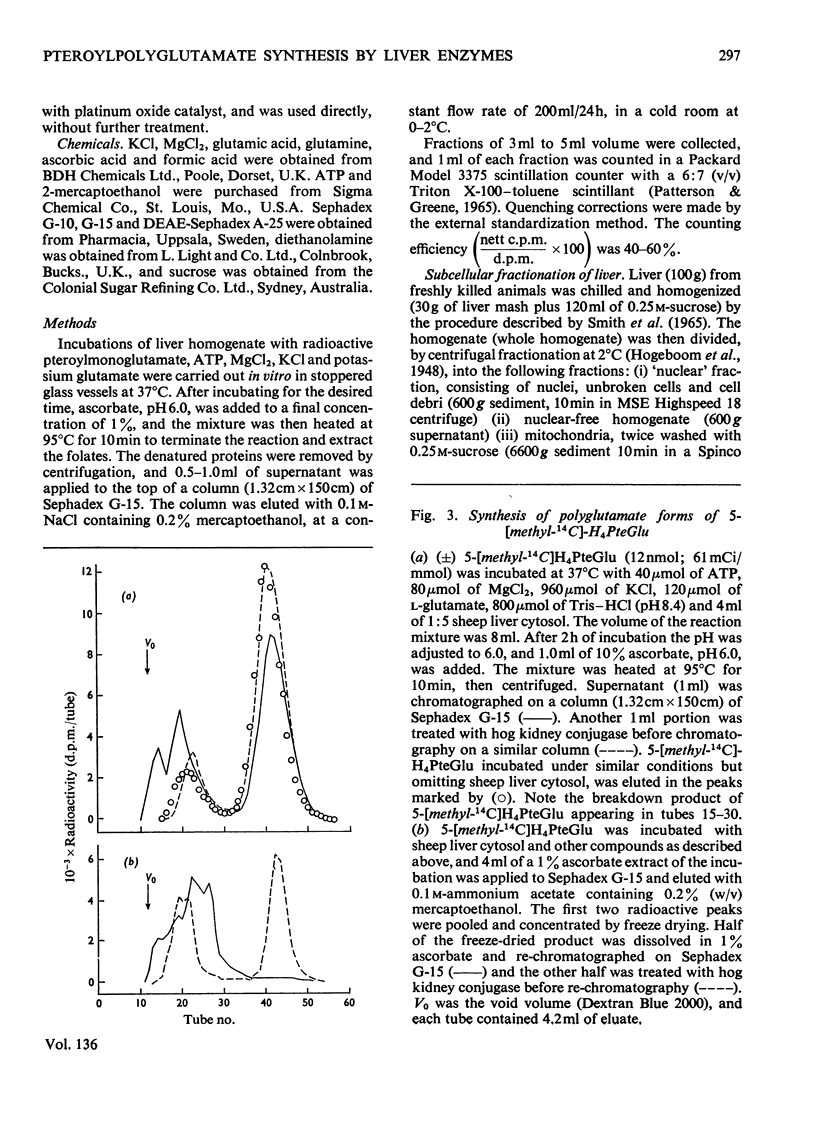
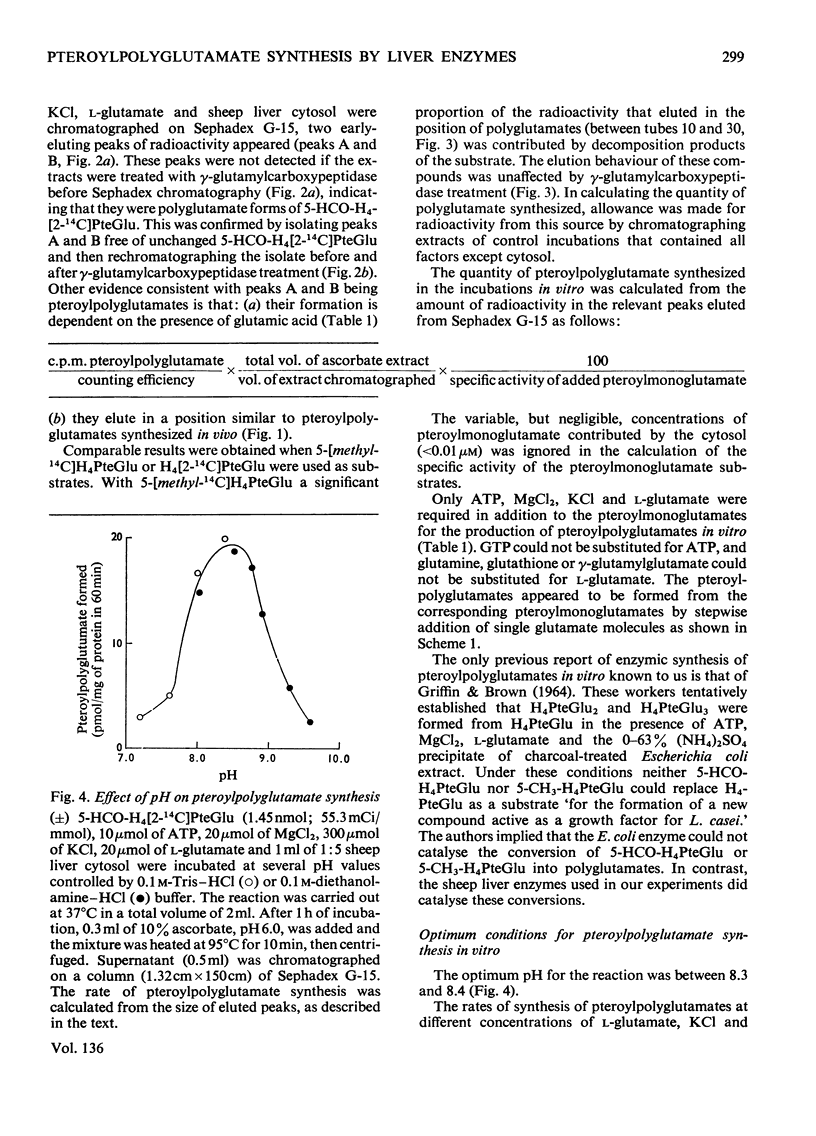
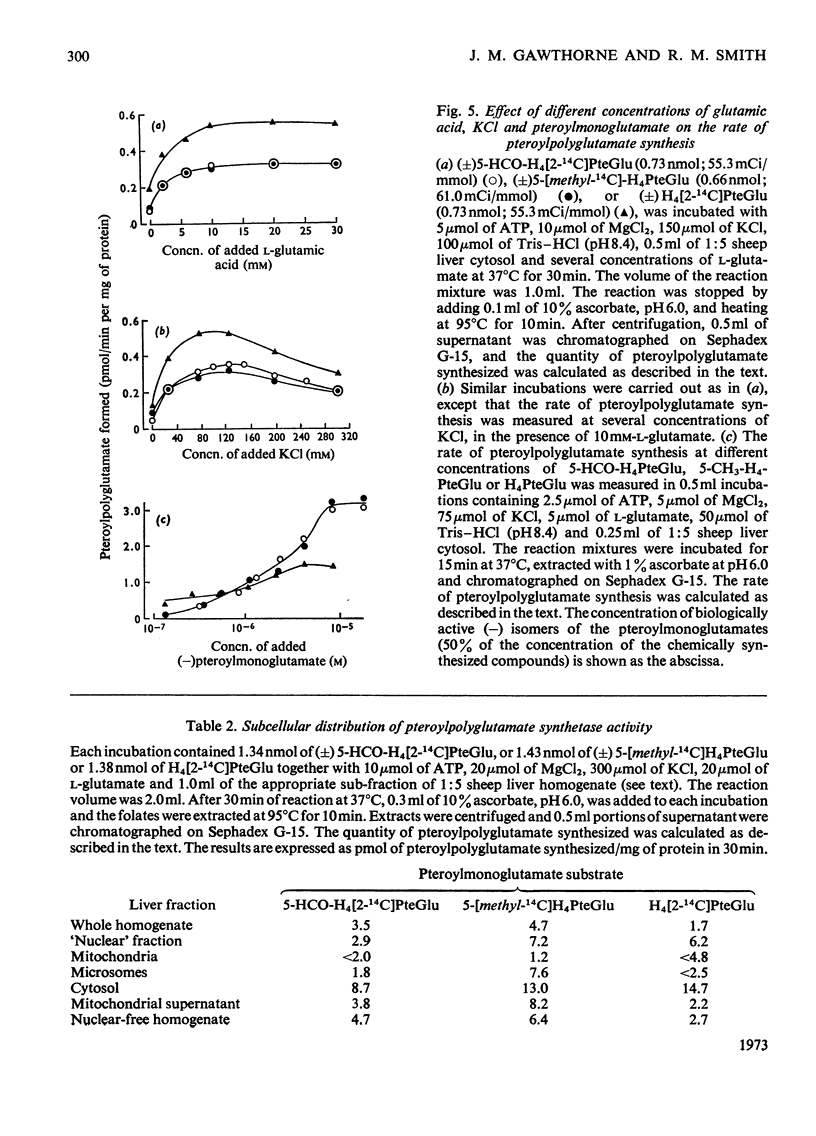
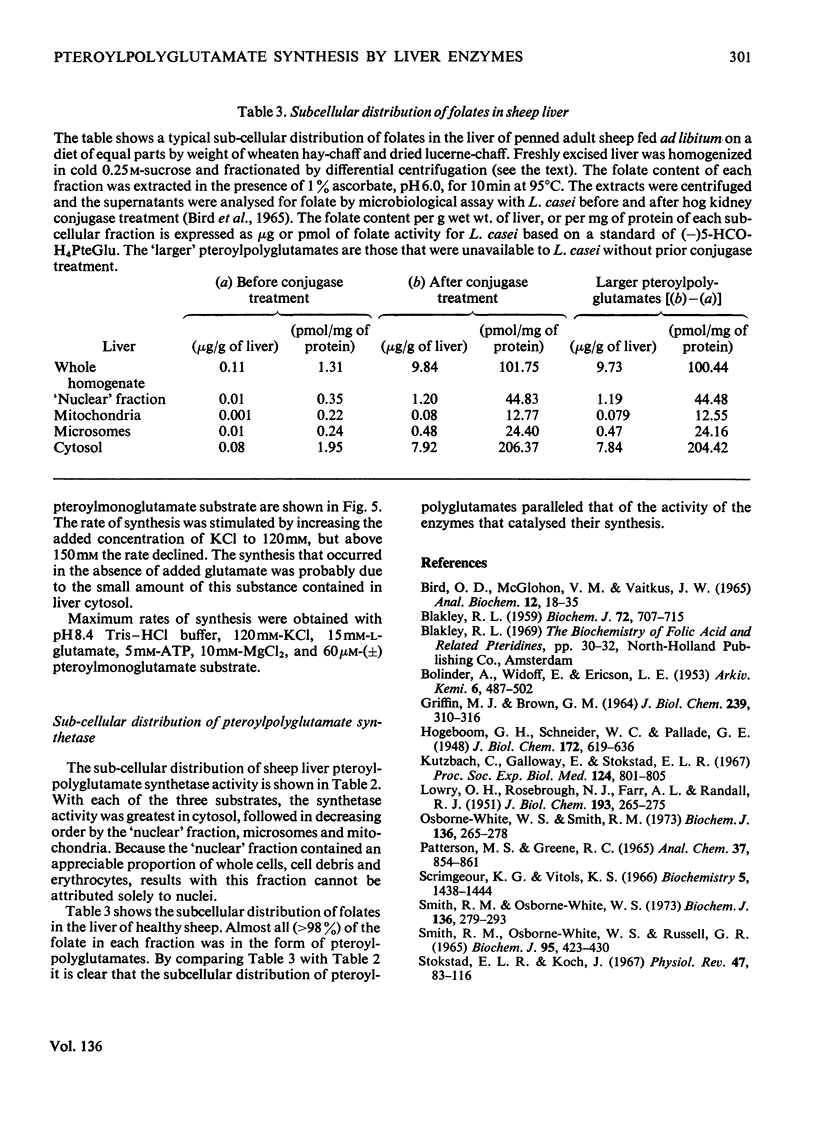
1. Sephadex G-15 was used to separate pteroylmonoglutamates from corresponding polyglutamate derivatives. 2. Pteroylpolyglutamates were formed when 5-formyltetrahydro[2-14C]pteroylglutamic acid, 5-[methyl-14C]tetrahydropteroylglutamic acid or tetrahydro[2-14C]pteroylglutamic acid was incubated at pH8.4 with ATP, MgCl2, KCl, l-glutamic acid and sheep liver cytosol. The γ-glutamyl side chain appeared to be lengthened by the stepwise addition of single glutamate moieties. 3. The subcellular distribution of pteroylpolyglutamates paralleled that of pteroylpolyglutamate synthetase activity, and followed the order cytosol>`nuclear' fraction>microsomal fraction>mitochondria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLAKLEY R. L. The reaction of tetrahydropteroylglutamic acid and related hydropteridines with formaldehyde. Biochem J. 1959 Aug;72:707–715. doi: 10.1042/bj0720707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird O. D., McGlohon V. M., Vaitkus J. W. Naturally occurring folates in the blood and liver of the rat. Anal Biochem. 1965 Jul;12(1):18–35. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIFFIN M. J., BROWN G. M. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF FOLIC ACID. III. ENZYMATIC FORMATION OF DIHYDROFOLIC ACID FROM DIHYDROPTEROIC ACID AND OF TETRAHYDROPTEROYLPOLYGLUTAMIC ACID COMPOUNDS FROM TETRAHYDROFOLIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:310–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutzbach C., Galloway E., Stokstad E. L. Influence of vitamin B12 and methionine on levels of folic acid compounds and folate enzymes in rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Mar;124(3):801–805. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne-White W. S., Smith R. M. Identification and measurement of the folates in sheep liver. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;136(2):265–278. doi: 10.1042/bj1360265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON M. S., GREENE R. C. MEASUREMENT OF LOW ENERGY BETA-EMITTERS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION BY LIQUID SCINTILLATION COUNTING OF EMULSIONS. Anal Chem. 1965 Jun;37:854–857. doi: 10.1021/ac60226a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrimgeour K. G., Vitols K. S. The reduction of folate by borohydride. Biochemistry. 1966 Apr;5(4):1438–1443. doi: 10.1021/bi00868a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. M., Osborne-White W. S. Folic acid metabolism in vitamin B12-deficient sheep. Depletion of liver folates. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;136(2):279–293. doi: 10.1042/bj1360279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. M., Osborne-White W. S., Russell G. R. Metabolism of propionate by sheep liver. Stimulation of the mitochondrial rate by factors from the cell sap. Biochem J. 1965 May;95(2):423–430. doi: 10.1042/bj0950423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokstad E. L., Koch J. Folic acid metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1967 Jan;47(1):83–116. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


