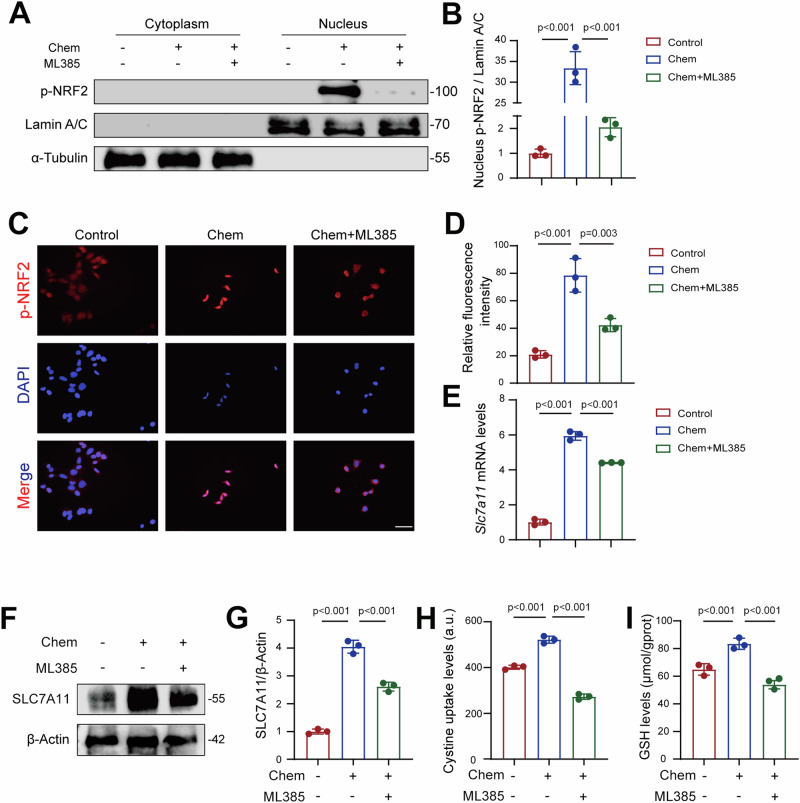
Fig. 8. Chemerin promotes NRF2 nuclear translocation to induce SLC7A11 transcription in renal tubular epithelial cells.
A NRF2 inhibition prevents chemerin-induced nuclear translocation of NRF2. TCMK-1 cells were treated with recombinant chemerin (20 ng/ml) and NRF2 inhibitor ML385 (10 μM) for 24 h. Cytoplasmic and nuclear protein samples were prepared for western blot analysis. Lamin A/C was used as a loading control for nuclear proteins, and α-Tubulin was used as a loading control for cytoplasmic proteins. n = 3 (independent experiments). B Quantification of NRF2 levels from the western blots shown in (A). C Representative immunofluorescence staining images of phosphorylated NRF2 (p-NRF2). Cell treatments were as described in (A). n = 3 (independent experiments). Scale bar = 50 μm. D Relative fluorescence intensity of p-NRF2 as shown in (C). E mRNA levels of SLC7A11 in TCMK-1 cells treated with the recombinant chemerin and ML385. Cell treatments were as described in (A). n = 3 (independent experiments). F Western blot analysis of SLC7A11 in TCMK-1 cells treated with Chemerin and ML385. Cell treatments were as described in (A). β-Actin was used a loading control. n = 3 (independent experiments). G Quantification of SLC7A11 from the western blots shown in (F). Cystine uptake (H) and GSH levels (I). Cell treatments were as described in (A). n = 3 (independent experiments). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001, by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.