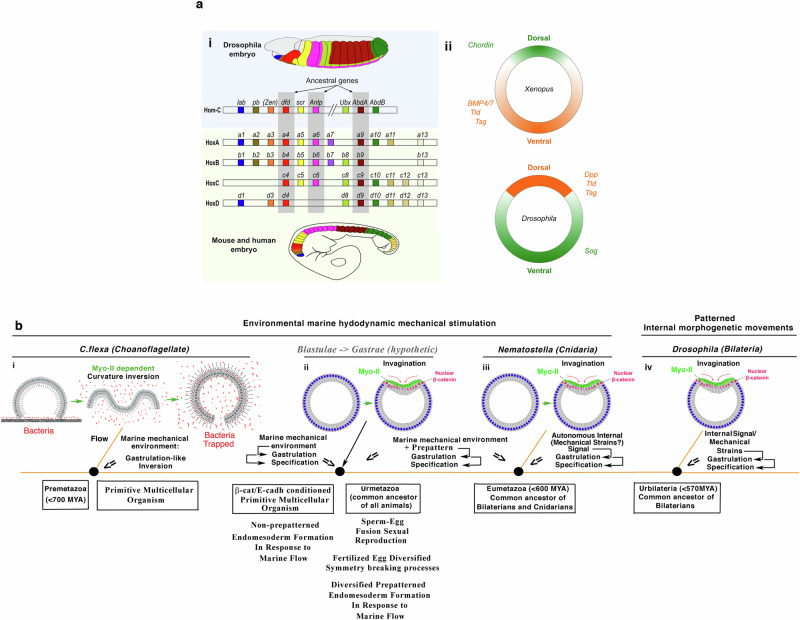
Fig. 6. Genetic and mechanotransductive common origin of Bilateria and of first multicellular animal organisms.
a Conservation of i Hox genes and of their expression along the anteroposterior axis of the embryo across species, here in Drosophila versus mouse and human embryos, ii and of embryonic early dorso-ventral patterning genes, inverted in vertebrates compared to insects (here in Xenopus and Drosophila early embryos). Adapted from16 and81. b Conservation of Myo-II-dependent hydrodynamic stimulation of i gastrulation-like inversion in C.flexa and of iii gastrulation in Nematostella, whose last common ancestor was a pre-metazoan dating back to at least 700 million years ago. ii Environmental hydrodynamic stimulation of endomesoderm morphogenesis and specification from β-cat/E-cadherin conditioned multicellular colony of cells, subsequently prepatterned after egg-sperm fusion sexual reproduction, having hypothetically led to the Gastrae (black arrow). iv Substitution of environmental mechanical strains by patterned internal mechanical strains stimulated gastrulation in Bilaterians such as Drosophila embryos, whose last common ancestor dates back to 570 million years ago. Adapted from86.