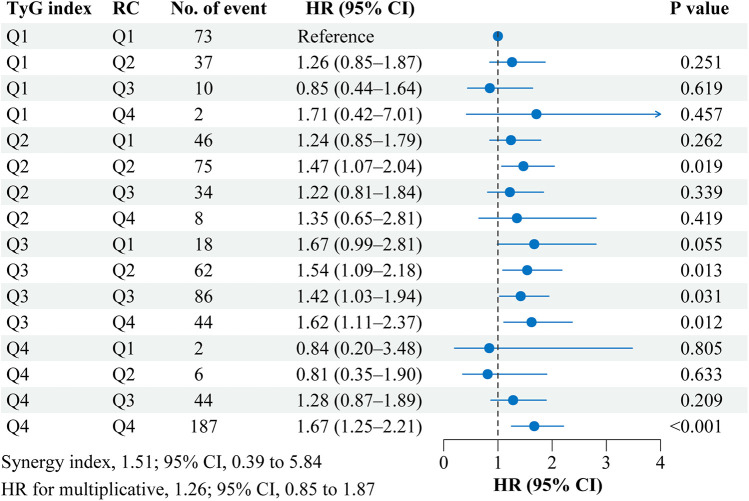
Figure 3.
Interaction and joint effects for triglyceride-glucose index and remnant cholesterol on stroke risk. Graphs show the interaction and joint effects of the TyG index and remnant cholesterol with stroke risk. The model was adjusted for age, gender, marital status, residence, education level, body mass index, smoking status, drinking status, diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, dyslipidemia, kidney disease, history of medication use for diabetes, history of medication use for hypertension, history of medication use for dyslipidemia, systole blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, HbA1c, hsCRP, and eGFR. Additive interaction was evaluated using synergy index (SI) between the TyG index and remnant cholesterol, and the additive interaction was statistically significant when its CI did not include 1. Multiplicative interaction was evaluated using HR for the product term between the TyG index and remnant cholesterol, and the multiplicative interaction was statistically significant when its CI did not include 1. CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; Q, quartile, RC, remnant cholesterol; TyG, triglyceride-glucose.