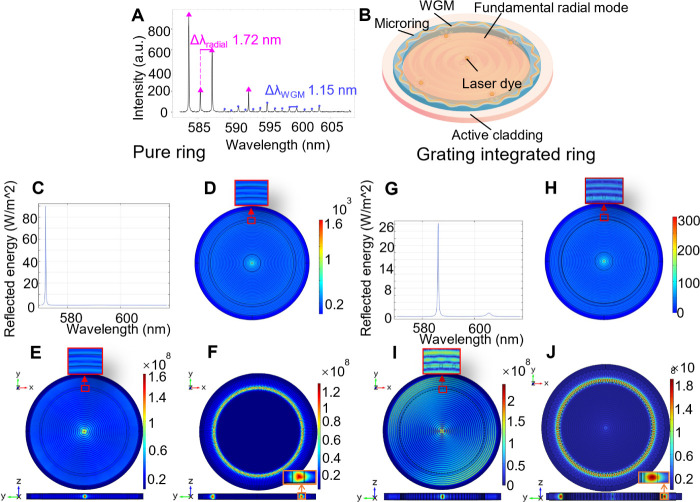
Figure 1.
(A) Spectrum of the active cladding microring laser with R = 25 μm, showing radial modes (magenta triangle), WGMs (blue dot). (B) Schematic of the coexistence of radial modes and WGMs. (C)–(J) Simulation results on active cladding microring, where (C)–(F) for pure ring: (C) dependence of reflectivity on wavelength, (D) intensity distribution of the light source formed by the active layer in the xy-plane at 572.25 nm, (E) intensity distribution of fundamental radial mode at 572.51 nm, and (F) intensity distribution of WGM at 602.25 nm. And (G)–(J) for grating integrated ring: (G) dependence of reflectivity on wavelength, (H) intensity distribution of the light source formed by the active layer in the xy-plane at 587.92 nm, (I) intensity distribution of fundamental radial mode at 587.79 nm, and (J) intensity distribution of WGM at 602.24 nm.