Figure 4. Molecular interactions of KP.3.1.1 RBD with hACE2.
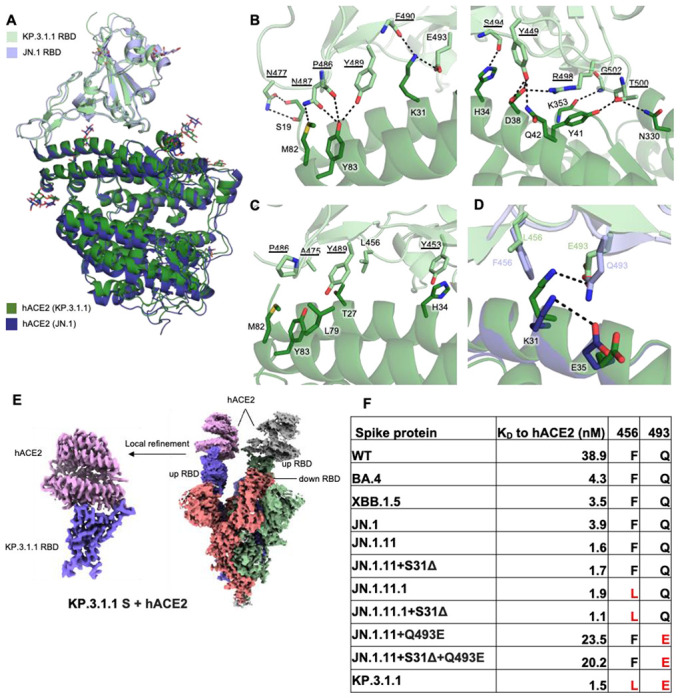
(A) Structural alignment of KP.3.1.1 RBD/hACE2 with JN.1 RBD/hACE2 (PDB ID: 8Y18)1 from cryo-EM structures of their spike proteins with hACE2 using RBD for alignment. Cα RMSD between the two RBDs is 0.9 Å. KP.3.1.1 RBD and hACE2 are colored in light green and green, respectively. JN.1 RBD and its hACE2 are colored in light blue and blue, respectively. (B) Molecular details of hydrophilic interactions between KP.3.1.1 RBD and hACE2. Conserved residues between KP.3.1.1 and JN.1 are underlined. Residues are numbered according to their positions on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein sequence. Hydrogen bonds and salt bridges are represented by black dashed lines. (C) Hydrophobic interactions between KP.3.1.1 RBD and hACE2. Aromatic and aliphatic residues are displayed. (D) Structural analysis of cooperative interactions between F456L, Q493E, and ACE2. F456 and Q493 in JN.1 RBD, and L456 and E493 in KP.3.1.1 are displayed. Two salt bridges between K31 and E35 in the JN.1 RBD/hACE2 complex (intrachain), and between K31 and E493 (interchain) in the KP.3.1.1 RBD/hACE2 complex, are shown as black dashed lines. (E) Left, cryo-EM density map corresponding to the KP.3.1.1 RBD/hACE2 interaction from focused local refinement of cryo-EM structure with spike protein and hACE2. Right, cryo-EM density of the entire KP.3.1.1 S/hACE2 complex. Maps are colored by chain with the three protomers of the spike trimer in blue, green, and salmon and hACE2 in pink and grey. (F) Binding affinity of hACE2 to recombinant spike proteins. Binding affinity is expressed as the nanomolar dissociation constant (KD). (See also figure S6).
