Figure 5. Structural details of S31Δ, N30 glycosylation, and BD55-1205 binding to KP.3.1.1 and other S31Δ mutants.
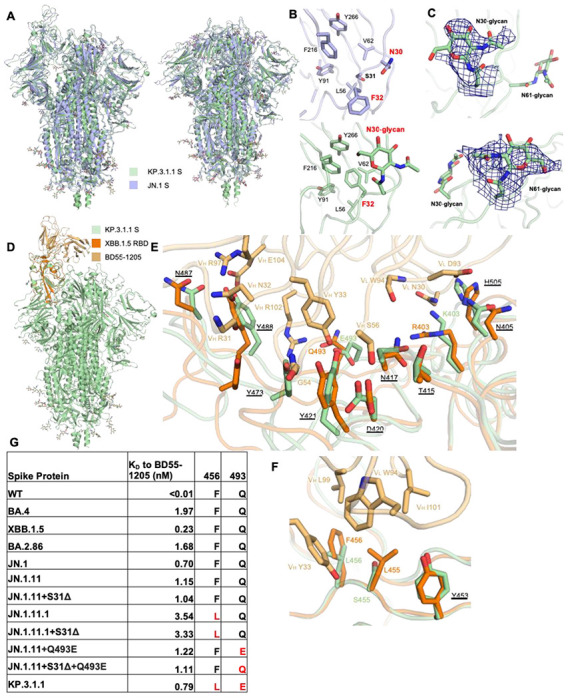
(A) Superimposed cryo-EM structures of KP.3.1.1 S and JN.1 S in both “One RBD Up” (PDB ID: 8Y5J)1 and “All RBD Down” (PDB ID: 8X4H)27 states. Cα RMSD’s are 1.1 Å and 0.9 Å respectively. KP.3.1.1 S and JN.1 S are colored light green and light blue, respectively. (B) Zoomed-in view around the N30 glycan site. Compared to the JN.1 S, S31Δ results in an F32 sidechain flip of 180° to now fit into the hydrophobic pocket formed by L56, V62, Y91, F216, and Y266. N30 is glycosylated in KP.3.1.1 S. (C) Zoomed-in view of N30 and N61 glycans with the cryo-EM density map in deep blue. (D) Superimposed structures of KP.3.1.1 S with the XBB.1.5 RBD/BD55-1205 complex (PDB ID: 8XE9)19 to identify possible interactions of BD55-1205 with KP.3.1.1 . KP.3.1.1 S, XBB.1.5 RBD, and BD55-1205 are colored in light green, orange, and light orange, respectively. (E, F) Zoomed-in view of the hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions between XBB.1.5 RBD and BD55-1205, respectively, Corresponding residues in KP.3.1.1 in the binding site are also displayed. Conserved residues between KP.3.1.1 and XBB.1.5 are underlined. (G) Binding affinity of BD55-1205 Fab to recombinant spike proteins. Binding affinity is expressed as the nanomolar dissociation constant (KD). (See also figure S7, S8, and S9).
