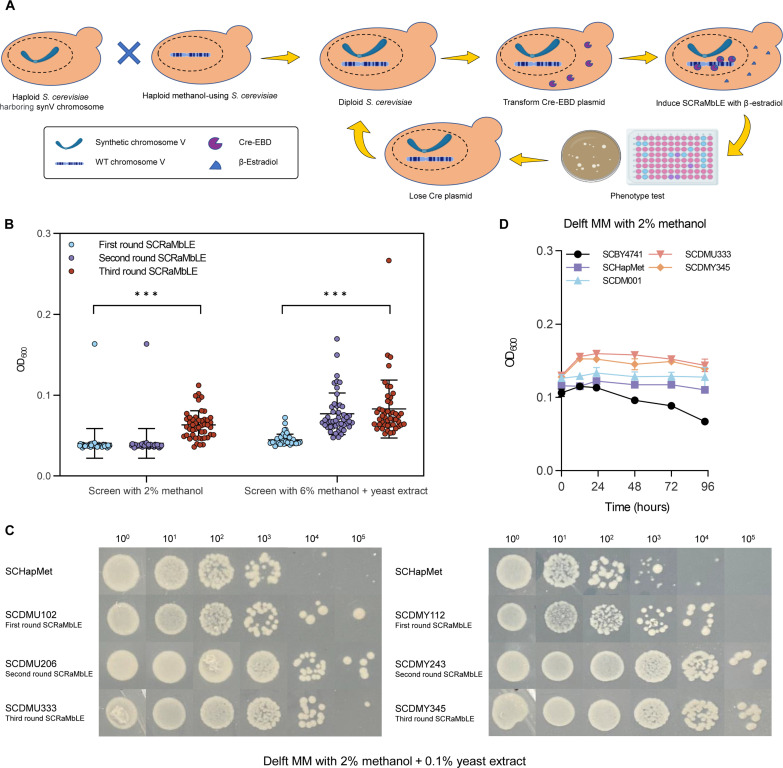
Fig. 1. Screening of synthetic methylotrophic S. cerevisiae by SCRaMbLE.
(A) Workflow for screening synthetic methylotrophs by SCRaMbLE. (B) Screening statistics of three rounds of SCRaMbLE. Error bars shown are mean and SD from the 47 samples in each round SCRaMbLE. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed student’s t test (***P < 0.001). (C) Serial dilution assay comparing the growth of an independent SCRaMbLEd isolate from each SCRaMbLE round with the original haploid methanol-using strain SCHapMet. SCDMU102, SCDMU206, and SCDMU333 are isolates screened on 2% methanol after one, two, and three rounds of SCRaMbLE, respectively. SCDMY112, SCDMY243, and SCDMY345 are isolates screened on 6% methanol + yeast extract after one, two, and three rounds of SCRaMbLE, respectively. (D) Growth curves of the wild-type (WT) S. cerevisiae (SCBY4741), haploid methanol-using strain (SCHapMet), diploid methanol-using strain (SCDM001), and SCRaMbLEd strain (SCDMU333 and SCDMY345) in Delft MM with 2% methanol. All data are presented as mean ± SD. Triplicate independent samples were adopted for each panel. For strains except SCBY4741, uracil (20 mg/liter) was supplemented in Delft MM to compensate for uracil auxotroph. For strain SCBY4741, uracil (20 mg/liter), histidine (20 mg/liter), leucine (100 mg/liter), and methionine (20 mg/liter) were supplemented in Delft MM.