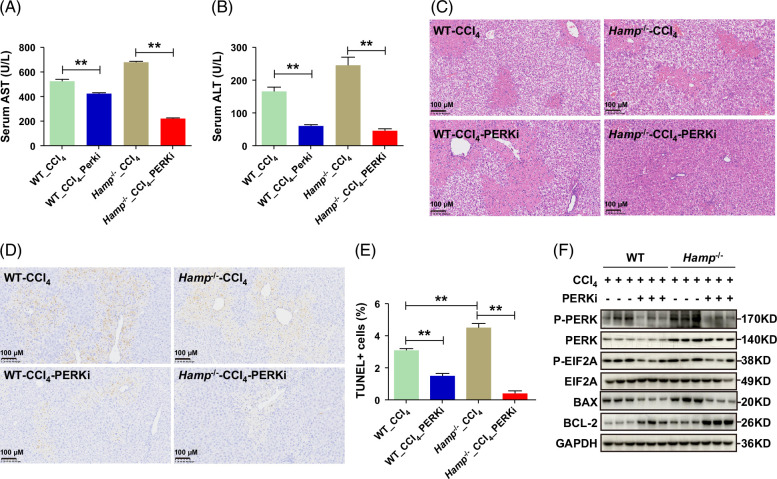
FIGURE 7.
The inhibition of PERK alleviates liver injury. (A, B) Levels of serum AST (A) and ALT (B) in WT and Hamp −/− mice with CCl4-induced liver injury after treatment with PERK inhibitor. (C) H&E staining of liver tissues from WT and Hamp −/− mice after treatment with PERK inhibitor in the CCl4-induced liver injury model. (D, E) TUNEL staining and quantification of apoptotic cells in liver tissues of WT and Hamp −/− mice after treatment with PERK inhibitor in the CCl4-induced liver injury model. (F) Protein expression levels of P-PERK, PERK, P-EIF2A, EIF2A, BAX, and BCL-2 in WT and Hamp −/− mice with CCl4-induced acute liver injury for 48 hours after treatment with PERK inhibitor. PERKi, PERK inhibitor. **p < 0.01, compared with control. Abbreviations: CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; H&E, hematoxylin-eosin; Hamp −/−, hepcidin knockout; TUNEL, TdT-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling; WT, wild type.