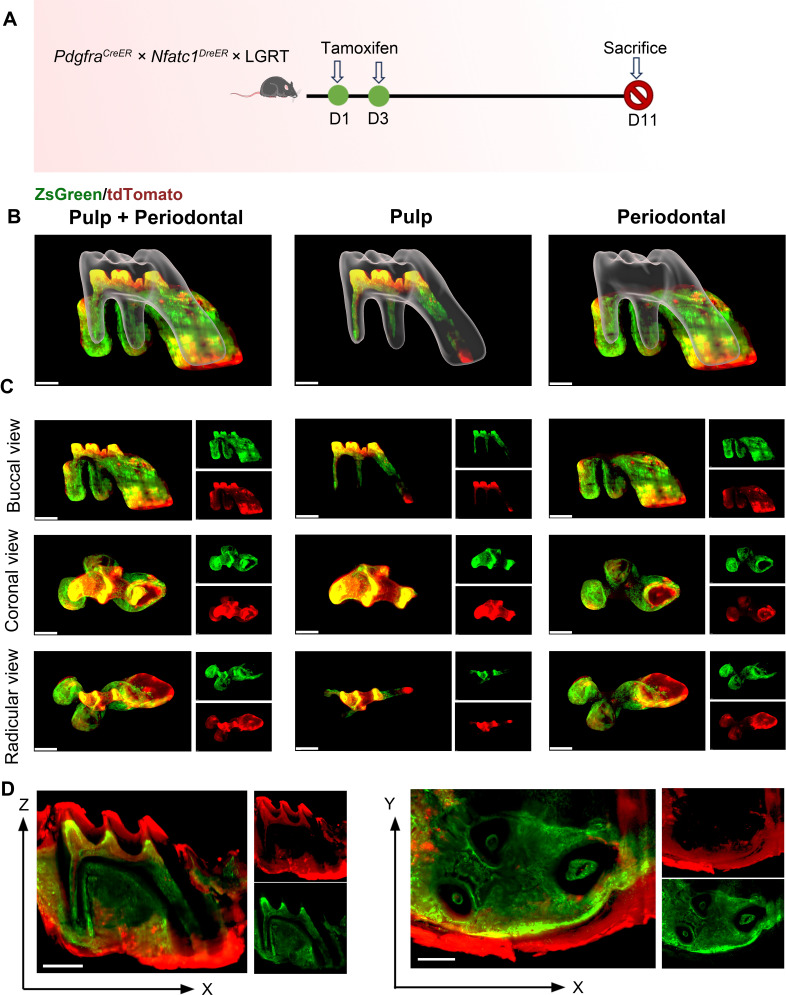
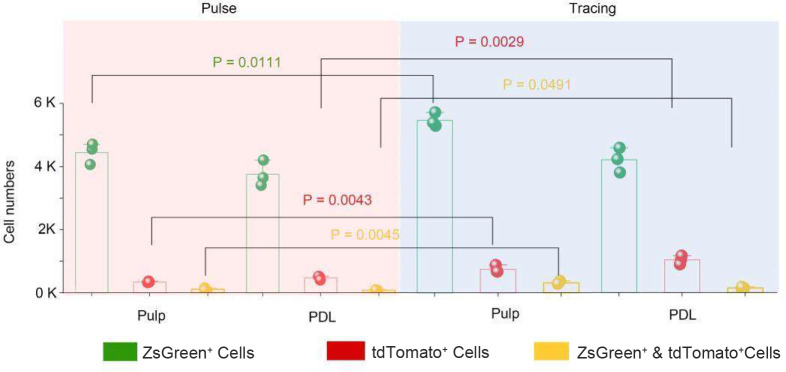
Figure 5. The observation of lineage tracing of PDGFR-α+ and NFATc1+ cells in M1 by whole-mount and high-speed imaging.
(A) The flowchart of tracing. The mice were administrated with tamoxifen at D1 and D3, and sacrificed at D11. (B) The 3D images of contoured M1 of maxilla, including pulp and PDL with virtual dentin shell (white) in buccal view (scale bar = 300 μm). (D) Image stack was displayed in buccal view, coronal view, and radicular view of pulp and PDL, respectively. (E) An optical slice was acquired on the X-Z (scale bar = 400 μm) and X-Y direction to display the pulp and PDL (scale bar = 300 μm).