Figure 3 –
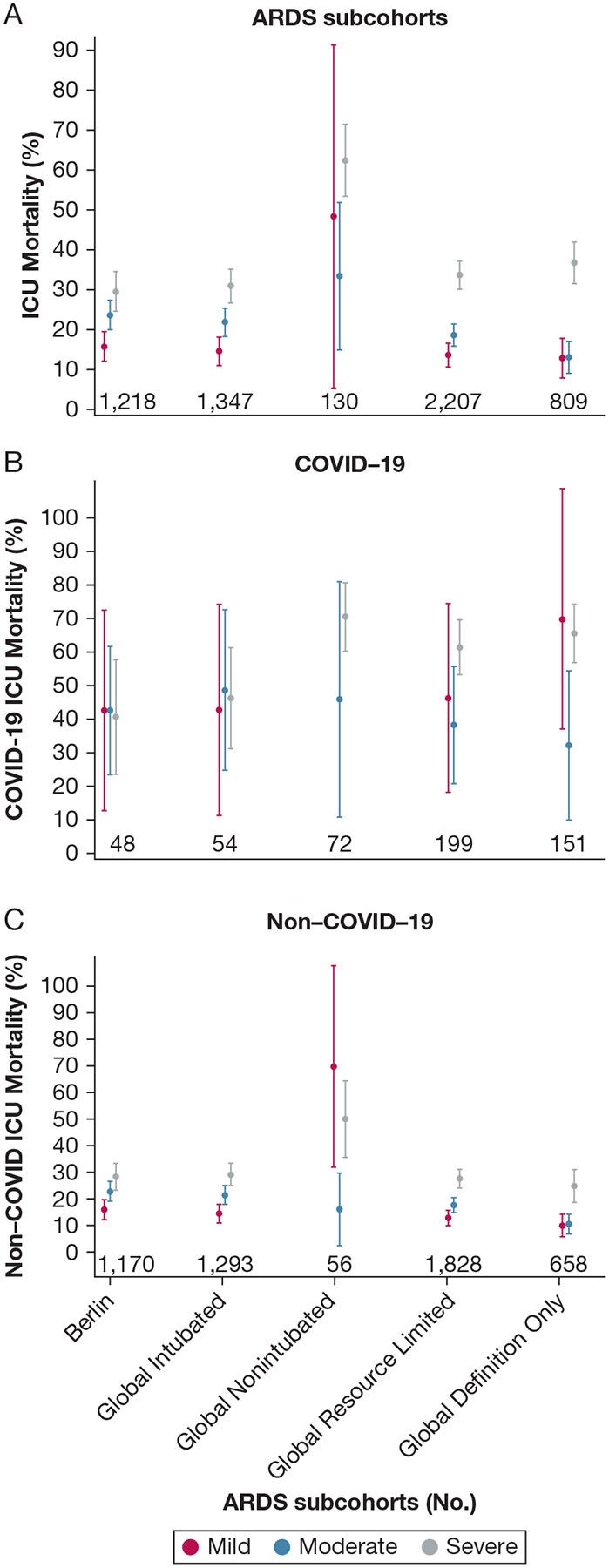
A-C, Graphs showing ICU mortality by the global definition of ARDS subcohorts, oxygenation severity levels, and COVID-19 status. A, Intubated patients in the global definition of ARDS cohort, similar to the highly overlapping the Berlin definition of ARDS cohort, showed worsening ARDS oxygenation severity classification associated with increased ICU mortality, and the global definition resource-limited settings modification ARDS cohort, similar to the substantially overlapping global definition-only ARDS cohort, showed a decrease and narrowing of ICU mortality outcomes between the mild and moderate levels and a widening and worsening of the severe level ICU mortality outcomes. Nonintubated patients in the global definition of ARDS cohort were too few for meaningful precision. B, C, Stratification by COVID-19 status showed the increased mortality of the severe level driven by patients with COVID-19 (B) and the decreased mortality in the mild and moderate levels driven by patients without COVID-19 (C).
