FIGURE 5.
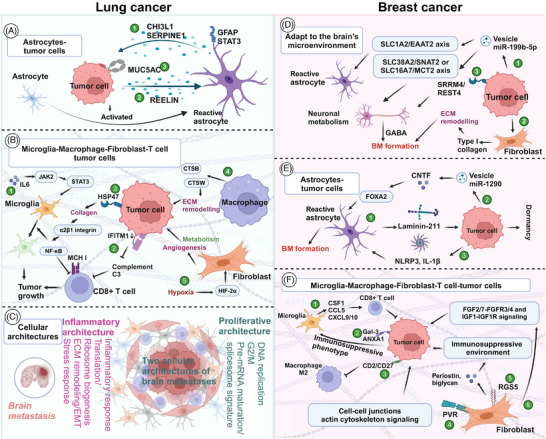
The colonization mechanism of tumor cells in the intracranial microenvironment. (A–C) Lung cancer. (A) Astrocytes–tumor cells interactions. (A①) The aggressive proliferation of metastatic brain tumor is linked to the release of CHI3L1 from p‐STAT3+ astrocytes. (A②) In SCLC, reelin is secreted to stimulate the recruitment of astrocytes, which subsequently leads to the secretion of SERPINE1 and other proteins by astrocytes, thereby promoting the growth of SCLC. (A③) Tumor cells interact with astrocytes, inducing an upregulation of MUC5AC expression in tumor cells and enhancing brain colonization. (B) Interactions between tumor cells and microglia, macrophage, fibroblast, and T cells. (B①) Increased IL6 regulates the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway to induce the anti‐inflammatory effect of microglia, thereby promoting the colonization of tumor cells. (B②) Low expression or loss of IFITM1 results in a decrease in complement component 3 and MHC I molecules, ultimately inhibiting the killing effect of CD8+ T cells. (B③) The HSP47–collagen axis achieves M2 polarization through the α2β1 integrin/NF‐κB pathway, leading to the upregulation of anti‐inflammatory cytokines and inhibiting the antitumor response of CD8+ T cell. (B④) High expression of cathepsins CTSB and CTSW in macrophages contributes to multiple tumor‐promoting processes including invasion and metastasis. (B⑤) Hypoxia mediates HIF‐2α, leading to CAFs undergoing a unique lineage transition. The transformed CAFs exhibit angiogenesis, trigger metabolic program rearrangement, and promote tumor cells growth. (C) Cellular architectures The proliferative BM functional archetypes are prominent in DNA replication, G2/M, and pre‐mRNA maturation as well as the spliceosome signature while the inflammatory BM functional archetypes are prominent in inflammatory response, ECM remodeling, and stress response ability. (D–F) Breast cancer. (D)Tumor cells adapt to the brain microenvironment. (D①) Tumor cells secrete vesicles rich in miR‐199b‐5p, which act on SLC1A2/EAAT2 axis to activate astrocytes and alter neuronal metabolism through SLC38A2/SNAT2 or SLC16A7/MCT2 axis. (D②) Tumor cells stimulate fibroblast secretion of type I collagen to reconstruct ECM and promote tumor growth. (D③) Tumor cells overexpress SRRM4/EST4, promoting GABA production and leading to tumorigenesis. (E) Astrocytes–tumor cells interactions. (E①) Astrocytes secrete Laminin‐211 to promote tumor cell dormancy. (E②) Tumor cells secrete vesicles rich in miR‐1290 to activate the CNTF–FOXA2 axis. (E③) Meanwhile, tumor cells increase NLRP3 and IL‐1β in astrocytes, which leads to the activation of astrocytes and promotes tumor metastasis. (F) Microglia–macrophage–fibroblast‐T cell‐tumor cells. (F①) Microglia secrete CSF1, CCL5, CXCL9/10 to activate CD8+T cells and kill tumor cells. (F②) Tumor cells overexpress Gal‐3 and ANXA1 to activate the immunosuppressive phenotype of microglia. (F③) Meanwhile, tumor cells expressing CD2/CD27 inhibit M2 type macrophage. (F④‐⑤) Fibrocytes activate cell junctions actin cytoskeleton signaling through PVR, and shape an immunosuppressive microenvironment by secreting periostin and biglycan through RGS5. (F⑥) Fibrocytes promote tumor growth through FGF2/7–FGFR3/4 and IGF1‐IGF1R signaling.
