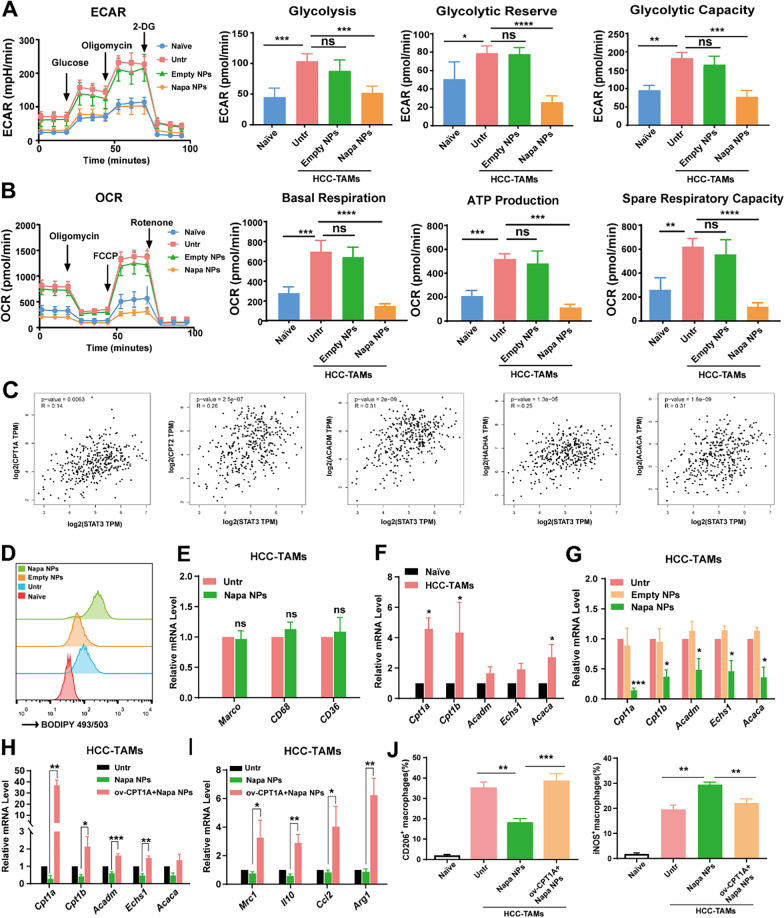
Fig. 7.
Napabucasin-PLGA NPs inhibit FAO in HCC-TAMs. A The levels of ECAR, glycolysis, glycolytic reserve, glycolytic capacity of HCC-TAMs treated as indicated for 24 h. B The levels of OCR, basal respiration, ATP production, spare respiratory capacity of HCC-TAMs treated as indicated for 24 h. C The analysis of correlation between FAO-related molecules and STAT3 in HCC through GEPIA 2 database. D The lipid levels of RAW264.7 cells cultured in medium (Naive) and HCC-TAMs treated as indicated were detected by flow cytometry. E The mRNA levels of CD36, CD69 and Macro in HCC-TAMs treated with Napabucasin-PLGA NPs or not were determined by RT-qPCR. F The mRNA levels of FAO-related genes in RAW264.7 cells cultured in medium (Naive) and HCC-TAMs were determined by RT-qPCR. G The mRNA levels of FAO-related genes in HCC-TAMs treated with Napabucasin-PLGA NPs or Empty NPs for 24 h were determined by RT-qPCR. H, I The mRNA levels of FAO-related (H) and M2 markers (I) in HCC-TAMs treated as indicated for 24 h were determined by RT-qPCR. J The levels of CD206, iNOS in HCC-TAMs treated as indicated for 24 h were measured by flow cytometry. Naive, RAW264.7 cells incubated in culture medium; Untr, untreated HCC-TAMs; Napa NPs, Napabucasin-PLGA NPs (3 μM); ov-CPTIA, HCC-TAMs over-express CPT1A. Data are shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ns, no significance