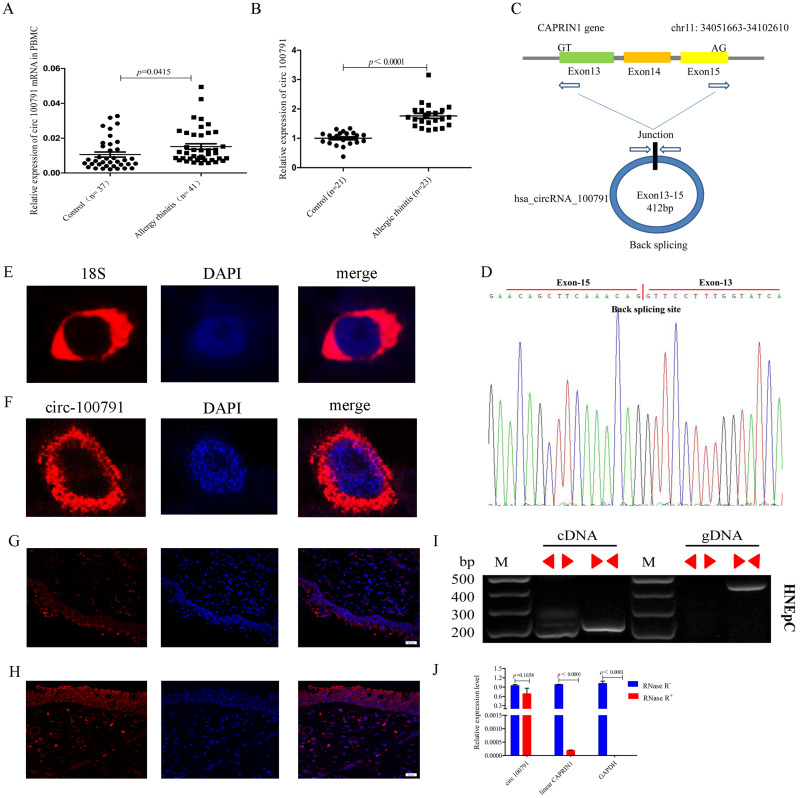
Figure 1.
Hsa_circ_100791 expression was increased in AR patients compared to healthy controls. (A and B) hsa_circ_100791 expression was elevated in both PBMCs and nasal mucosa from AR patients compared to healthy controls. (C) Schematic diagram illustrating that hsa_circ_100791 is generated from exons 13, 14, and 15 of the CAPRIN1 gene. (D) Sanger sequencing of hsa_circ_100791 PCR products, with the red arrow indicating the head-to-tail splicing site. (E and F) FISH analysis showing abundant expression of 18S and hsa_circ_100791 in the cytoplasm of human nasal epithelial cells (HNEpCs). Nuclei were stained with DAPI, and 18S and hsa_circ_100791 were labeled with Cy3. (G and H) FISH analysis demonstrating the abundant expression of hsa_circ_100791 in the cytoplasm of nasal mucosa from both healthy controls and AR patients. (I) PCR amplification of hsa_circ_100791 using convergent and divergent primers on cDNA and genomic DNA from HNEpCs. Results indicate successful amplification of hsa_circ_100791 with divergent primers using cDNA, but not with genomic DNA. (J) qRT-PCR analysis of RNA extracted from HNEpCs treated with RNase R, showing that hsa_circ_100791 is more stable than linear CAPRIN1 and GAPDH. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
Abbreviations: AR, allergic rhinitis; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; HNEpCs, human nasal epithelial cell line; SEM, standard error of the mean.