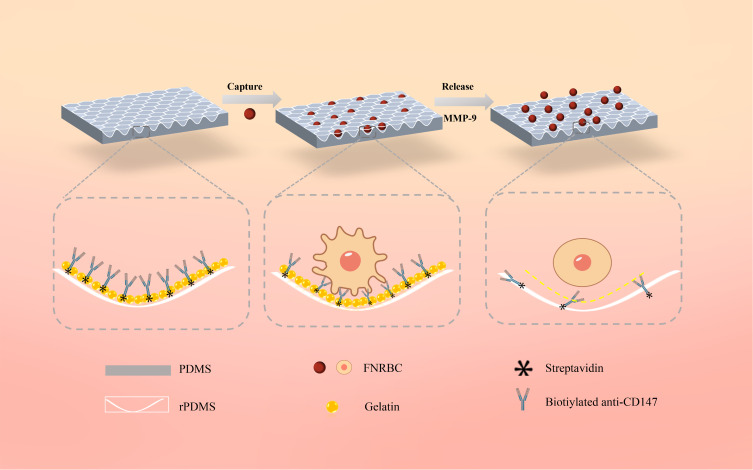
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the fetal cell separation and release mechanism utilizing GNPs-rPDMS technology. The red rose petal morphology is replicated onto PDMS, which, adorned with GNPs, forms a concave structure to furnish an expanded array of binding sites for the capture antibody (anti-CD147), thereby amplifying the affinity between fNRBCs and the substrate. Post cell capture, the GNPs are selectively degraded by an MMP-9 solution, facilitating the isolation and retrieval of intact cells.