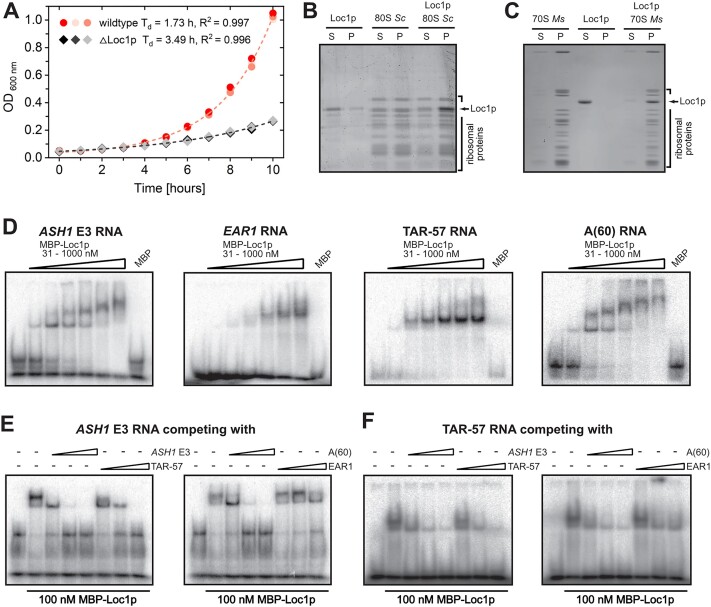
Figure 1.
Loc1p binds directly to ribosomes and unspecifically to RNA. (A) Comparison of doubling time of wild-type (S288C) and loc1Δ strains. loc1Δ cells show a severe growth delay (n = 3). Analytical ultracentrifugation of S. cerevisiae (B) and M. smegmatis (C) ribosomes and His6-tagged Loc1p reveals a co-enrichment of Loc1p with ribosomes in the pellet. In the absence of ribosomes, Loc1p is mainly found in the supernatant fraction of the sucrose cushion. (D) EMSAs with Loc1p and radioactively labeled ASH1 E3 localization element (LE), EAR1 LE, HIV-TAR stem–loop and poly-A60 RNA reveal unspecific binding in the nanomolar range. (E, F) Competition EMSAs with 100 nM MBP-Loc1p, 5 nM radioactively labeled RNA, and 10-, 100- and 500-fold excess of cold competitor RNA. Experiments show that ASH1 E3, TAR-57 and poly-A60 can compete for Loc1p interaction with ASH1 E3 (E) or TAR-57 (F).