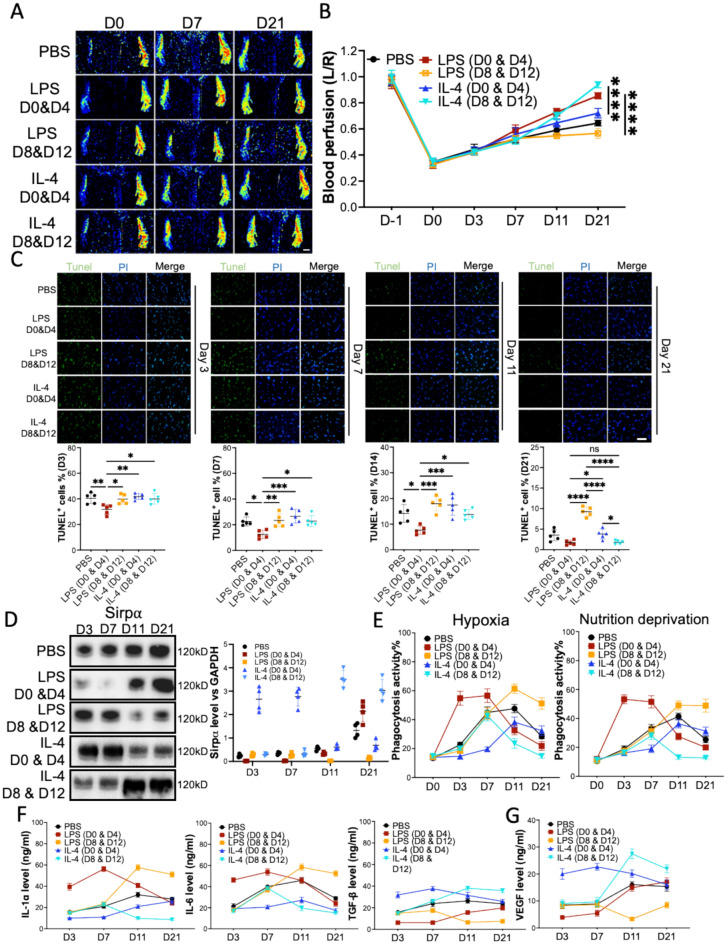
Fig. 2.
LPS and IL-4 promoted angiogenesis in mouse hindlimb ischemia in a time-dependent manner. After left artery ligation, the mice received PBS, LPS, and IL-4 intramuscularly injections at various times. A, B Laser speckle data showing the relative level of blood perfusion in the hind paws of mice that received various treatments on the indicated days (scale bar: 1000 µm). C The percentages of dead cells in gastrocnemius muscles from the mice on D3, D7, D14, and D21 post-surgery, scale bar: 100 µm. D The level of Sirpα in the macrophages collected from adductor muscles of the mice (n = 3). E The phagocytosis of pHrodo Red-labeled hypoxia or nutrition deprivation induced apoptotic mCMVECs by the macrophages from adductor muscles of the mice. Total 5000 cells were gated and analyzed. F, G IL-1α, IL-6, TGF-β (F), and growth factors (G) secreted from the macrophages that were collected from adductor muscles of the mice on the indicated days, were measured using ELISA. PBS, LPS D0 & D4 or IL-4 D0 & D4: the mice received PBS, LPS or IL-4 intramuscular injection on day 0 and day 4 post-surgery. LPS D8 & D12 or IL-4 D8 & D12: the mice received LPS or IL-4 intramuscular injection on day 8 and day 12 post-surgery. Data is analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey multiple range test and expressed as mean ± SD of n = 5, unless specified. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001****p < 0.0001. ns, non-significant