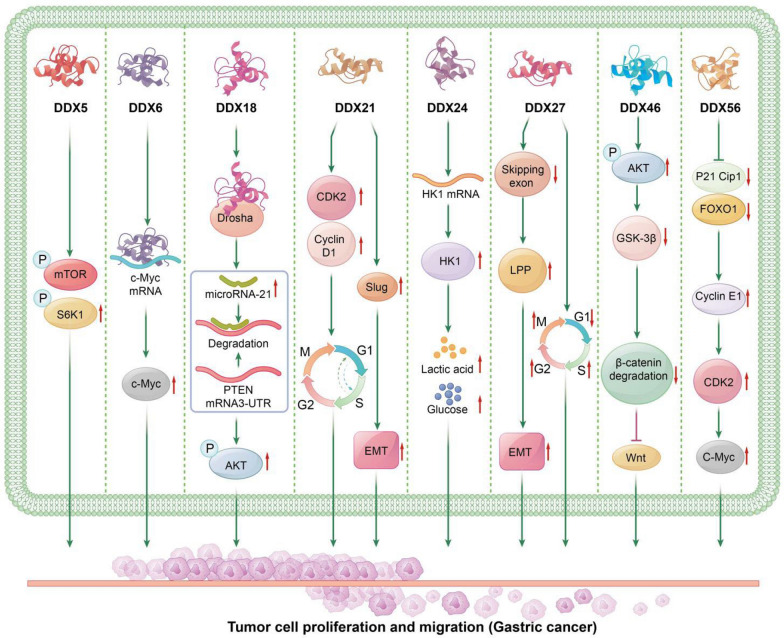
Fig. 3.
The Role of DEAD-Box Helicases in Gastric Cancer: DDX5: DDX5 increases the expression of p-mTOR and p-S6K1, promoting the growth of gastric cancer. DDX6: DDX6 binds to c-Myc mRNA, enhancing the expression of c-Myc protein, which promotes cell proliferation and the progression of gastric cancer. DDX18: DDX18 interacts with Drosha as a component of the protein complex, promoting the maturation of microRNA-21. MicroRNA-21 binds to the 3´-UTR of PTEN, leading to PTEN mRNA degradation and subsequent AKT phosphorylation, thereby promoting gastric cancer progression. DDX21: DDX21 promotes gastric cancer progression by upregulating Cyclin D1 and CDK2 levels, increasing the G1/S phase transition in gastric cancer cells. Additionally, DDX21 upregulates the expression of Slug, further promoting gastric cancer progression. DDX24: DDX24 positively regulates the level of HK1 by stabilizing HK1 mRNA at the transcriptional level, thereby enhancing glucose uptake and lactate production in gastric cancer cells, contributing to tumor progression. DDX27: DDX27 regulates LPP protein expression by reducing the SE event on the third exon of LPP transcripts, enhancing the translation of functional domain-containing LPP protein. This regulation via the DDX27/LPP/EMT axis promotes gastric cancer progression. DDX27 also reduces the proportion of cells in the G1 phase while increasing the proportion in the S and G2/M phases, thereby regulating the cell cycle and promoting cell proliferation and tumor progression in gastric cancer. DDX46: DDX46 promotes AKT phosphorylation and increases GSK-3β phosphorylation, leading to decreased GSK-3β-mediated β-catenin degradation and promoting gastric cancer progression through the Wnt signaling pathway. DDX56: DDX56 inhibits the expression of FOXO1 and p21 Cip1, thereby activating the downstream cyclin E1/CDK2/c-Myc signaling pathway, which promotes gastric cancer progression