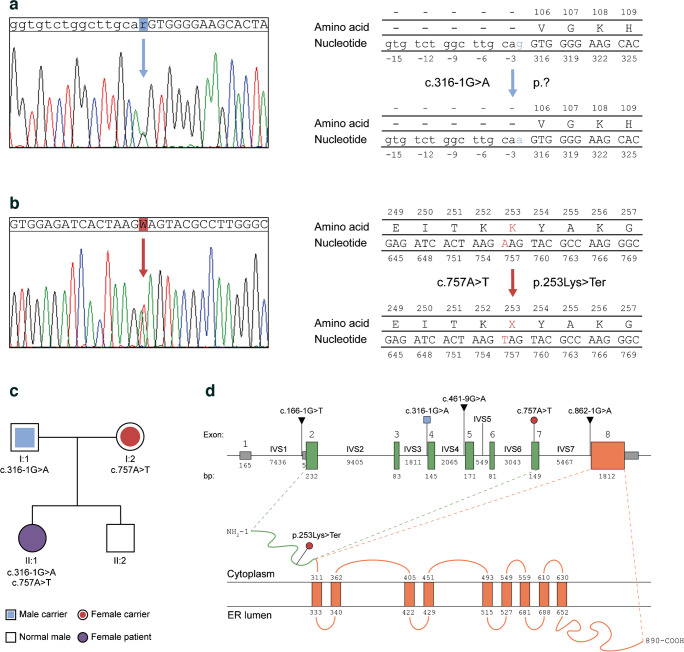
Fig. 1.
(a, b) Sanger sequencing chromatograms showing the heterozygous c.316-1G>A transition and the c.757A>T transversion in the WFS1 gene of the patient. The modified nucleotides are highlighted in blue and red, respectively, as well as the resulting amino-acid substitution in the protein sequence, if known. (c) Genetic pedigree of the patient’s family. The first line below each symbol represents generation and identification number. The heterozygous mutations found in the patient’s father and mother are reported; the patient’s brother carries no mutated allele. (d) Schematic representation of WFS1 gene and wolframin protein. The exons 1 (non-coding, grey boxes), 2–7 (encoding the N-terminal domain of wolframin, green boxes) and 8 (encoding the transmembrane and C-terminal domains of wolframin, orange box) are reported. The genomic position of the patient’s WFS1 mutations are highlighted and colour-coded as in (a, b). The previously reported ASS variants are reported as well. The N-terminal domain (green) and transmembrane/C-terminal domains (orange) are shown along with the c.757A>T transversion introducing a premature stop codon