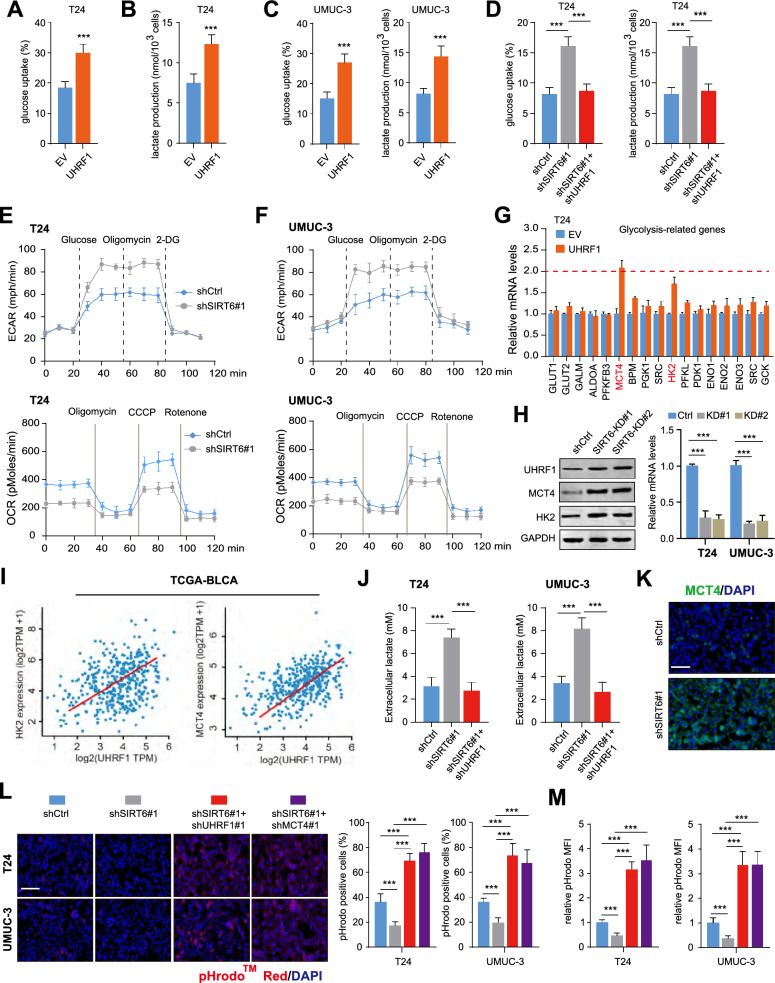
Fig. 5.
UHRF1 regulates glycolysis and lactate secretion in SIRT6-KD BLCA cells. A Overexpression of UHRF1 induced glucose uptake (left) and lactate production (right) in T24 cells. B Overexpression of UHRF1 induced glucose uptake (left) and lactate production (right) in UMUC-3 cells. (C) UHRF1 overexpression enhanced the glucose uptake and lactate production in T24 cells. D UHRF1-KD reduced glucose uptake and lactate production in SIRT6-KD T24 cells. E–F The ECAR profile was monitored in SIRT6-KD T24 (E) and UMUC-3 (F) cells with a Seahorse XF24 analyser for 100 min. The metabolic inhibitors were injected sequentially at different time points as indicated. G MCT4 and HK2 were screened as UHRF1-regulated genes. The expressions of a panel of glucose metabolism-related genes were detected by RT-qPCR analysis in UHRF1-overexpressing and control cells. H Western blotting and RT-qPCR analysis were used to detect MCT4/HK2 levels in T24 or UMUC-3 cells with or without SIRT6 knockdown. I Correlation analysis was calculated to determine UHRF1 and MCT4/HK2 expressions in TCGA-BLCA cohort. J Extracellular lactate levels of SIRT6 deficient cell lines with or without UHRF1-KD (n = 3). K Immunofluorescence staining of MCT4 in control SIRT6-KD tumors. Bar, 100 μm. (n = 3). L-M Intracellular pH was detected by pHrodo Red, and representative images were shown in indicated cells with or without UHRF1/MCT4-KD. Bar, 100 μm. (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns no significance