Abstract
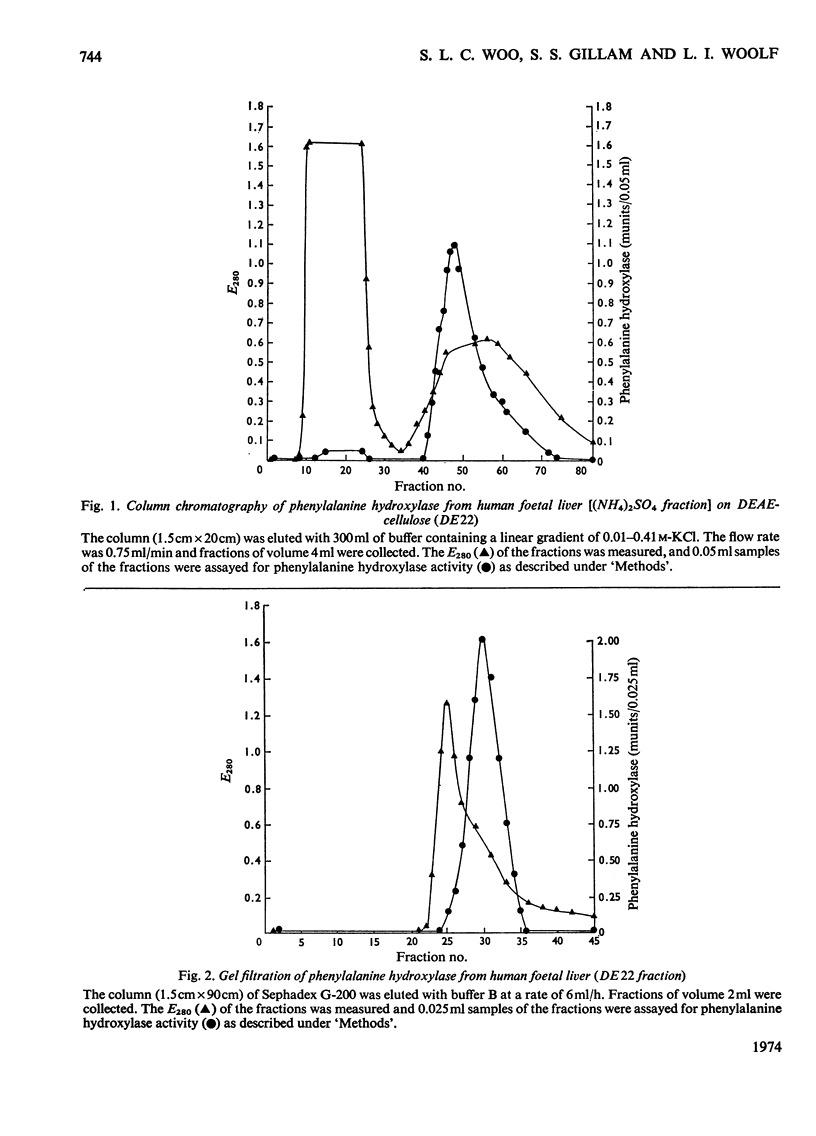
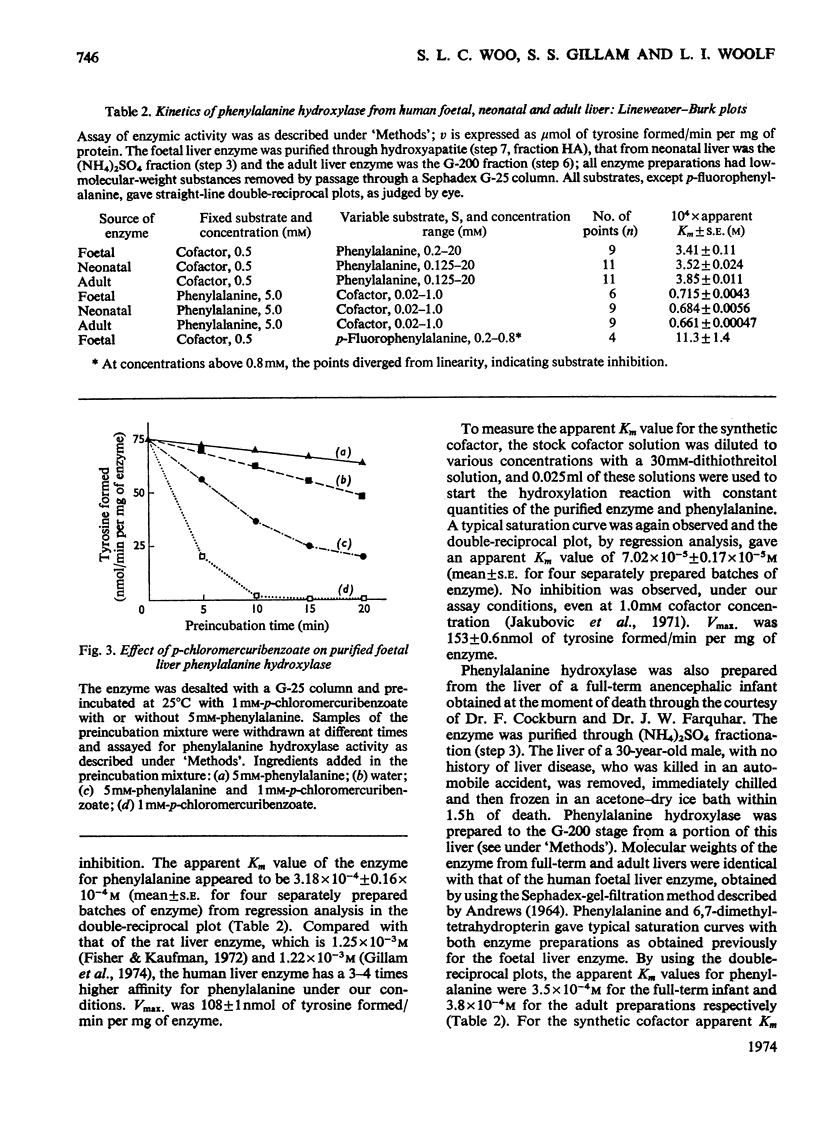
Phenylalanine hydroxylase was prepared from human foetal liver and purified 800-fold; it appeared to be essentially pure. The phenylalanine hydroxylase activity of the liver was confined to a single protein of mol.wt. approx. 108000, but omission of a preliminary filtration step resulted in partial conversion into a second enzymically active protein of mol.wt. approx. 250000. Human adult and full-term infant liver also contained a single phenylalanine hydroxylase with molecular weights and kinetic parameters the same as those of the foetal enzyme; foetal, newborn and adult phenylalanine hydroxylase are probably identical. The Km values for phenylalanine and cofactor were respectively one-quarter and twice those found for rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase. As with the rat enzyme, human phenylalanine hydroxylase acted also on p-fluorophenylalanine, which was inhibitory at high concentrations, and p-chlorophenylalanine acted as an inhibitor competing with phenylalanine. Iron-chelating and copper-chelating agents inhibited human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Thiol-binding reagents inhibited the enzyme but, as with the rat enzyme, phenylalanine both stabilized the human enzyme and offered some protection against these inhibitors. It is hoped that isolation of the normal enzyme will further the study of phenylketonuria.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERS R. F., Jr, SIZER I. W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barranger J. A., Geiger P. J., Huzino A., Bessman S. P. Isozymes of phenylalanine hydroxylase. Science. 1972 Feb 25;175(4024):903–905. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4024.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brase D. A., Westfall T. C. Stimulation of rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase activity by derivatives of vitamin E. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1185–1191. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90836-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connellan J. M., Danks D. M. Demonstration of two forms of phenylalanine hydroxylase in human liver obtained at autopsy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 12;293(1):48–55. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. B., Kaufman S. The stimulation of rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase by phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2250–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. B., Kirkwood R., Kaufman S. Rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase, an iron enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5161–5167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Kaufman S. Some characteristics of partially purified human liver phenylalanine hydroxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 12;293(1):56–61. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90375-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillam S. S., Woo S. L., Woolf L. I. The isolation and properties of phenylalanine hydroxylase from rat liver. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):731–739. doi: 10.1042/bj1390731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guroff G., Rhoads C. A. Phenylalanine hydroxylase from Pseudomonas species (ATCC 11299a). Purification of the enzyme and activation by various metal ions. J Biol Chem. 1967 Aug 25;242(16):3641–3645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubovic A. Phenylalanine-hydroxylating system in the human fetus at different developmental ages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 22;237(3):469–475. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubovic A., Woolf L. I., Chan-Henry E. The inactivation of phenylalanine hydroxylase by 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6,7-dimethyltetrahydropteridine and the aerobic oxidation of the latter. The effects of catalase, dithiothreitol and reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):563–568. doi: 10.1042/bj1250563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S., Fisher D. B. Purification and some physical properties of phenylalanine hydroxylase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4745–4750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. The phenylalanine hydroxylating system from mammalian liver. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1971;35:245–319. doi: 10.1002/9780470122808.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITOMA C. Studies on partially purified phenylalanine hydroxylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Feb;60(2):476–484. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90453-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourian A., Goddard J., Puck T. T. Phenylalanine hydroxylase activity in mammalian cells. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Apr;73(2):159–170. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040730210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Hoch F. L. ZINC, A COMPONENT OF YEAST ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Jun 15;41(6):327–338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.6.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAALKES T. P., UDENFRIEND S. A fluorometric method for the estimation of tyrosine in plasma and tissues. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Nov;50(5):733–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


