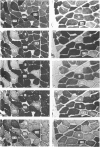
Abstract
Samples of longissimus and multifidi muscles at the thoracic and lumbar levels of the spine were examined histochemically on autopsy specimens from 21 adult male subjects (aged 22 to 46 years) and on biopsies from 17 adult patients during surgery for disorders of the lumbar intervertebral disc. In the superficial and deep thoracic muscles, 74% of fibres were of the Type I variety. In the lumbar region, Type I fibres amounted to 57% in the superficial, and to 63% in the deep muscles. The diameter of Type I fibres was significantly greater than that of Type II fibres.
Full text
PDF

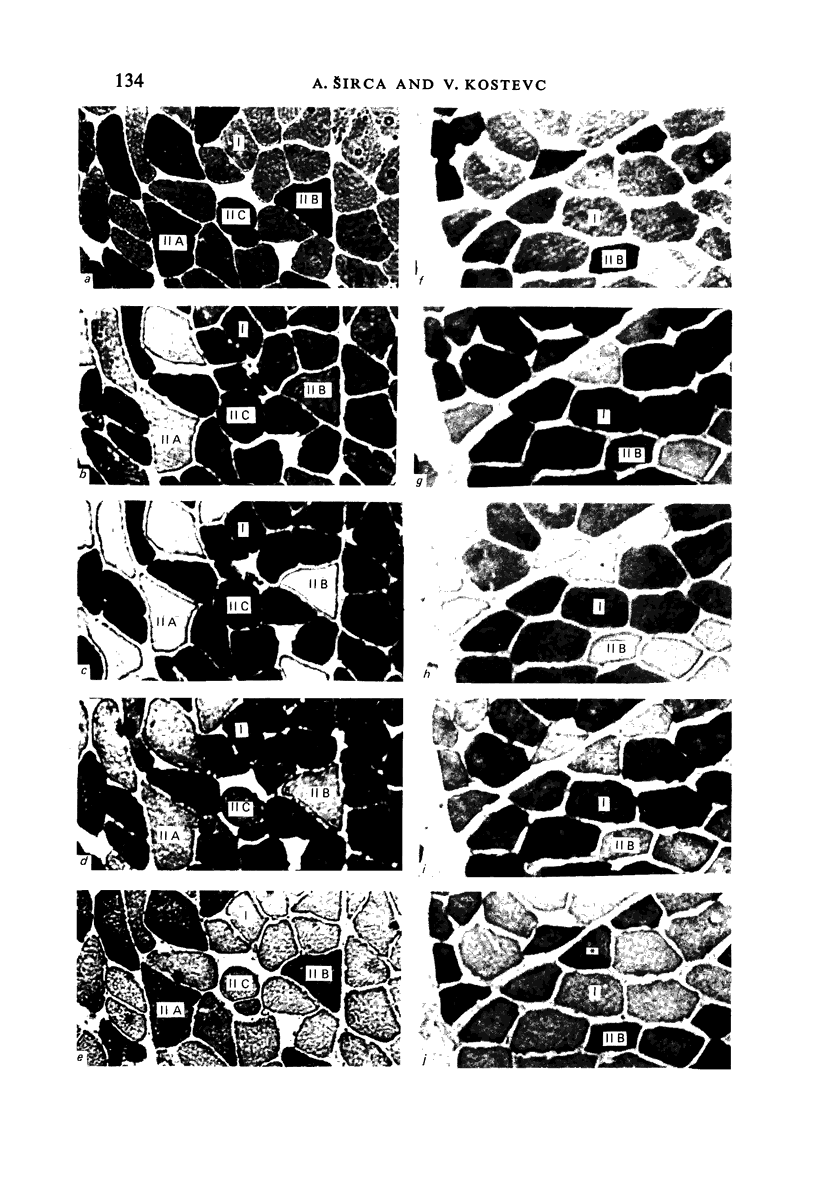



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagnall K. M., Ford D. M., McFadden K. D., Greenhill B. J., Raso V. J. A comparison of vertebral muscle fiber characteristics between human and monkey tissue. Acta Anat (Basel) 1983;117(1):51–57. doi: 10.1159/000145770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Engel W. K. The histographic analysis of human muscle biopsies with regard to fiber types. 1. Adult male and female. Neurology. 1969 Mar;19(3):221–233. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.3.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Kaiser K. K. Three "myosin adenosine triphosphatase" systems: the nature of their pH lability and sulfhydryl dependence. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 Sep;18(9):670–672. doi: 10.1177/18.9.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgerton V. R., Smith J. L., Simpson D. R. Muscle fibre type populations of human leg muscles. Histochem J. 1975 May;7(3):259–266. doi: 10.1007/BF01003594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson O., Eriksson A., Ringqvist M., Thornell L. E. The reliability of histochemical fibre typing of human necropsy muscles. Histochemistry. 1980;65(3):193–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00493169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler M. W., Jowett R. L., Troup J. D. Myosin ATPase activity in multifidus muscle from cases of lumbar spinal derangement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1975 May;57(2):220–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollnick P. D., Sjödin B., Karlsson J., Jansson E., Saltin B. Human soleus muscle: a comparison of fiber composition and enzyme activities with other leg muscles. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Apr 22;348(3):247–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00587415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSEPH J., McCOLL I. Electromyography of muscles of posture: posterior vertebral muscles in males. J Physiol. 1961 Jun;157:33–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. A., Polgar J., Weightman D., Appleton D. Data on the distribution of fibre types in thirty-six human muscles. An autopsy study. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Jan;18(1):111–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson B. The functions of individual muscles in the lumbar part of the spinae muscle. Electromyography. 1970 Jan-Apr;10(1):5–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J., Dorovini-Zis K. Types of human intrafusal muscle fibers. Muscle Nerve. 1979 Nov-Dec;2(6):437–451. doi: 10.1002/mus.880020605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell L. C., Carlson D. S., Brangwyn C. E. Lack of 'acid reversal' of myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase in masticatory muscle fibres of rhesus monkeys. Histochem J. 1980 Mar;12(2):209–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01024551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACHLAS M. M., TSOU K. C., DE SOUZA E., CHENG C. S., SELIGMAN A. M. Cytochemical demonstration of succinic dehydrogenase by the use of a new p-nitrophenyl substituted ditetrazole. J Histochem Cytochem. 1957 Jul;5(4):420–436. doi: 10.1177/5.4.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVIKOFF A. B., SHIN W. Y., DRUCKER J. Mitochondrial localization of oxidative enzymes: staining results with two tetrazolium salts. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Jan;9:47–61. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PADYKULA H. A., HERMAN E. Factors affecting the activity of adenosine triphosphatase and other phosphatases as measured by histochemical techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 May;3(3):161–169. doi: 10.1177/3.3.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polgar J., Johnson M. A., Weightman D., Appleton D. Data on fibre size in thirty-six human muscles. An autopsy study. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Jul;19(3):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90094-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringqvist M. Histochemical enzyme profiles of fibres in human masseter muscles with special regard to fibres with intermediate myofibrillar ATPase reaction. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Feb;18(2):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulemana C. A., Suchenwirth R. Topische Unterschiede in der enzymhistologischen Zusammensetzung der Skelettmuskulatur. Untersuchungen an 5 Skelettmuskein von Verstorbenen ohne neuromuskuläre Erkrankungen. J Neurol Sci. 1972 Aug;16(4):433–444. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(72)90049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trontelj J. V., Pecak F., Dimitrijević M. R. Segmental neurophysiological mechanisms in scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1979 Aug;61-B(3):310–313. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.61B3.479254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignon C., Pellissier J. F., Serratrice G. Further histochemical studies on masticatory muscles. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Mar;45(2-3):157–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATTENBERG L. W., LEONG J. L. Effects of coenzyme Q10 and menadione on succinic dehydrogenase activity as measured by tetrazolium salt reduction. J Histochem Cytochem. 1960 Jul;8:296–303. doi: 10.1177/8.4.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters R. L., Morris J. M. Electrical activity of muscles of the trunk during walking. J Anat. 1972 Feb;111(Pt 2):191–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]