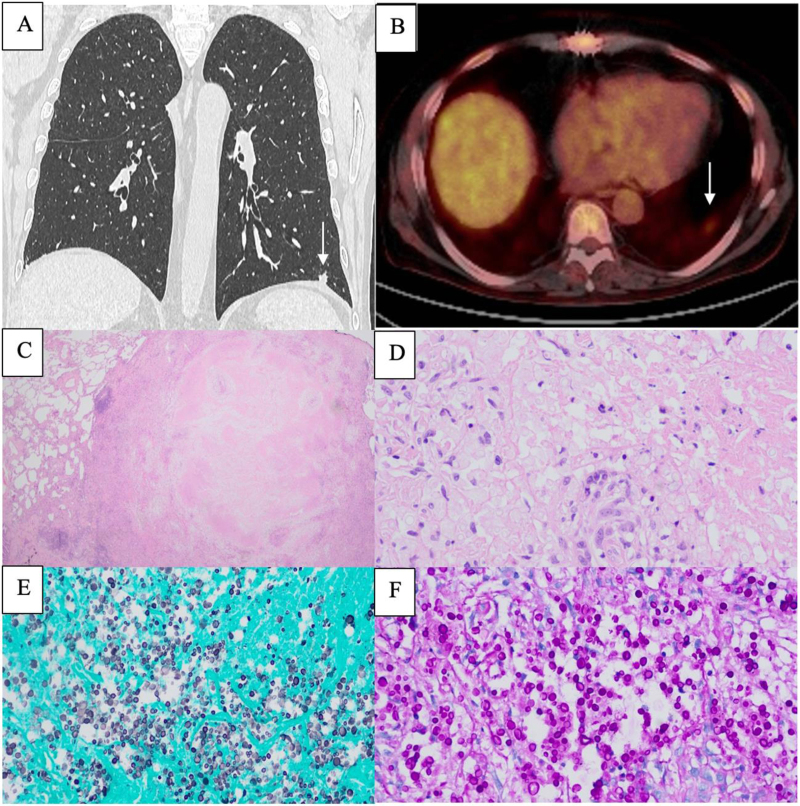
Fig. 1.
(A) Chest computed tomography scan, coronal axis, with left lower lobe pulmonary nodule (arrow). (B) 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography with pathological metabolism of the pulmonary nodule (arrow). (C) Microscopic section of the atypical lung resection, low-power view (H&E, 2×) shows necrotic epithelioid granulomatous inflammation, with normal lung parenchyma visible on the left side. (D) High-power view (H&E, 40×) reveals encapsulated yeast-like fungal structures. These fungal structures were positively stained with immunohistochemical techniques: (E) Grocott stain (40×) and (F) periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) reaction (40×).