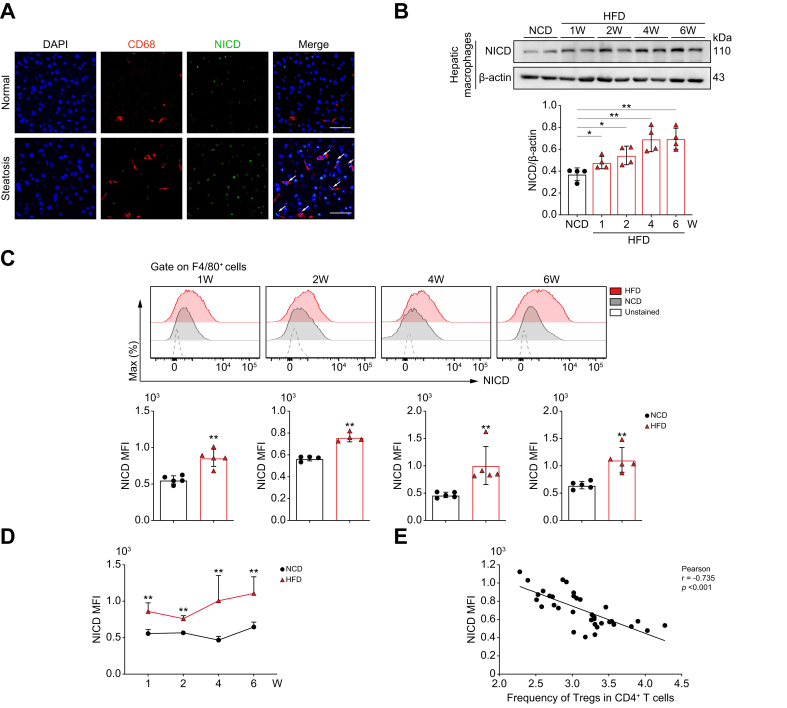
Fig. 2.
Hepatic macrophage Notch1 activation is negatively correlated with the frequency of hepatic CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs in hepatic steatosis.
(A) Representative pictures of IF staining for NICD in CD68+ cells from liver tissues of patients with or without hepatic steatosis (scale bar: 50 μm). WT C57BL/6 mice were fed with NCD or HFD. (B) Western blot analysis of NICD expression in hepatic macrophages isolated from mice fed a NCD or HFD (four 4/group). (C) Notch1 activation in hepatic macrophages was examined by flow cytometry at different time points (four or five/group). (D) Dynamic changes in the level of Notch1 activation in hepatic macrophages of mice fed a NCD or HFD for 1, 2, 4, and 6 weeks. (E) Relationship between the level of Notch1 activation in hepatic macrophages and frequency of hepatic CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs (38/group). Values represent means ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by a 2-tailed unpaired Student t test: ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01. Abbreviations: HFD, high-fat diet; IF, immunofluorescence; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; NCD, normal chow diet; NICD, Notch1 intracellular domain; Treg, regulatory T cell; WT, wild-type.