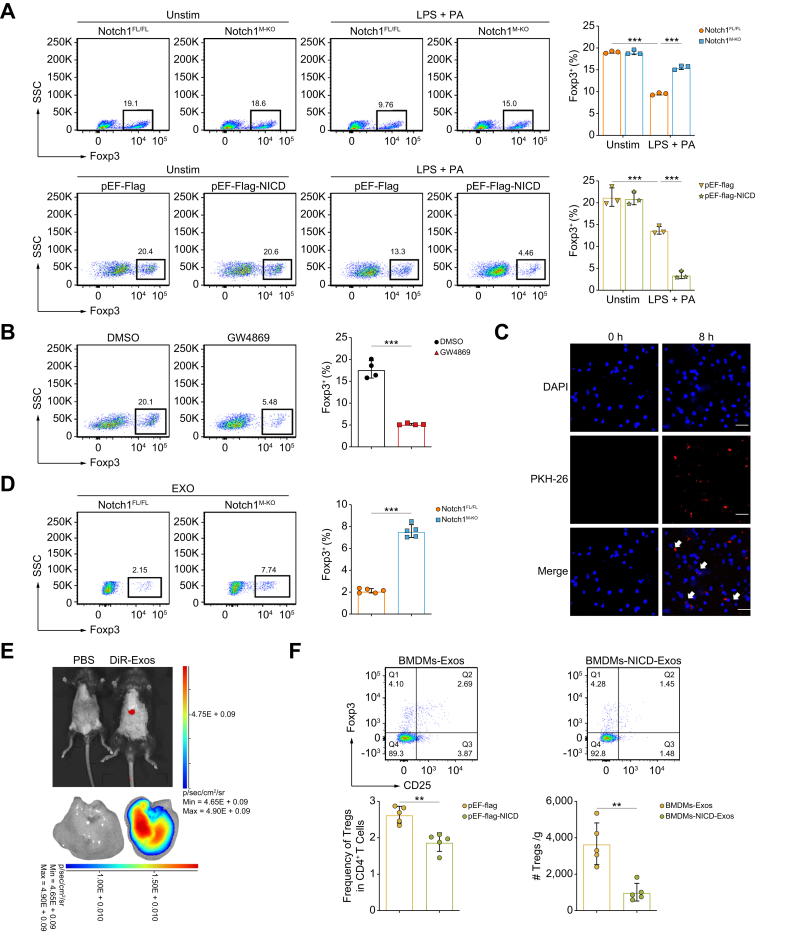
Fig. 5.
Exos from Notch1-activated macrophages impede Treg differentiation.
BMDMs from Notch1FL/FL and Notch1M-KO mice and pEF-Flag-NICD or pEF-Flag transfected BMDMs were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) and PA (250 μM) or PBS for 12 h and then co-cultured with naïve CD4+ T cells for 3 days. (A) Induction of Foxp3+ Tregs was analyzed by flow cytometry (three/group). (B) Naïve CD4+ T cells were co-cultured with BMDMs treated with GW4869 (5 μM) for 3 days, and the induction of Foxp3+ Tregs was detected by flow cytometry (four/group). (C) BMDM-Exos were labeled with PKH26 (red) and then co-cultured with naïve CD4+ T cells for 8 h. The resulting T cells were collected for fluorescence confocal microscopy to detect Exo uptake and their nuclear location was determined by DAPI (blue) staining (scale bar: 25 μm). (D) BMDMs from Notch1FL/FL and Notch1M-KO mice were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) and PA (250 μM) for 12 h. Naïve CD4+ T cells were co-cultured with BMDM-Exos for 3 days, and induction of Foxp3+ Tregs was detected by flow cytometry (five/group). (E) Small animal in vivo imaging was used to detect the distribution of DiR-labeled Exo fluorescence signals in vivo. (F) Exos were extracted from BMDMs transfected with pEF-Flag-NICD or pEF-Flag after LPS + PA stimulation, and their concentrations were measured using BCA. BMDM-Exos at a dose of 200 μg/mouse were injected via the tail vein into mice fed a HFD for 1 week, followed by another week of HFD feeding. Flow cytometry was used to detect the proportion and number of intrahepatic Tregs mice. Values represent means ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by (A) one-way ANOVA and Tukey's test or (B,D) 2-tailed unpaired Student t test. ∗∗∗p <0.001. Abbreviations: BMDM, bone marrow-derived macrophage; Exo, exosome; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NICD, Notch1 intracellular domain; Notch1FL/FL, floxed Notch1; Notch1M-KO, myeloid-specific Notch1-knockout; PA, palmitic acid; Treg, regulatory T cell.