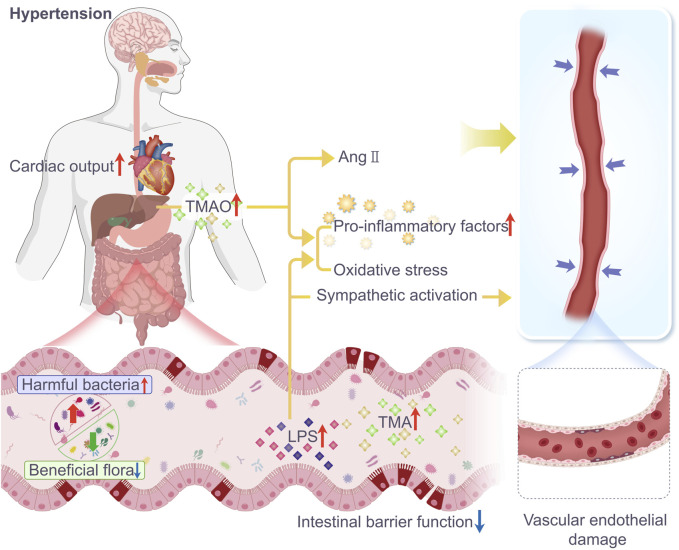
FIGURE 1.
In patients with hypertension, the diversity and abundance of gut microbiota are significantly reduced, and there is a clear dysfunction of the intestinal barrier. The number of beneficial bacteria decreases, while the number of harmful bacteria and gut microbiota metabolites TMAO and LPS increase, leading to a reduction in tight junction proteins in the intestine and increased intestinal permeability. TMAO, a metabolite generated by intestinal microbes from TMA, is oxidized in the liver. It can cause hypertension by enhancing the vasoconstrictive effects of angiotensin II, increasing inflammatory factors, and inducing oxidative stress leading to vasoconstriction. LPS can exacerbate hypertension by releasing pro-inflammatory factors, inducing oxidative stress, and activating the sympathetic nervous system, leading to vasoconstriction and increased cardiac output.