FIGURE 1.
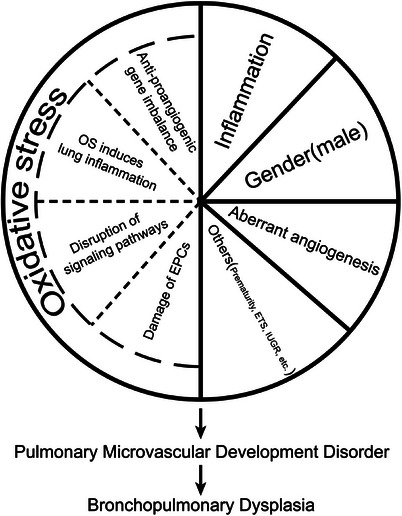
Pathological mechanism of pulmonary microvascular dysplasia. EPCs, endothelial progenitor cells; OS, oxidative stress; ETS, environmental tobacco smoke; IUGR, intrauterine growth restriction.

Pathological mechanism of pulmonary microvascular dysplasia. EPCs, endothelial progenitor cells; OS, oxidative stress; ETS, environmental tobacco smoke; IUGR, intrauterine growth restriction.