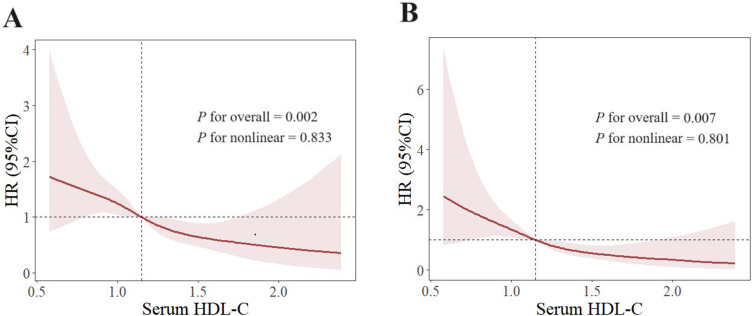
Figure 3.
Restricted cubic spline of the association between serum HDL-C and gout flares. Spline plot of serum HDL-C level and gout flares. (A) Original model to explore relationship between serum HDL-C and gout flares without adjustment. (B) Adjusted for disease duration, palpable tophus, BMI, eGFR, serum urate, ALT, AST, blood glucose, triglyceride, LDL-C. The hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated with cox regression model. The dashed lines were x–value when HR was 1. BMI, body mass index; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. P for overall < 0.05 means serum HDL-C and gout flares had correlation. P for nonlinear > 0.05 means correlation between serum HDL-C and gout flares was linear.