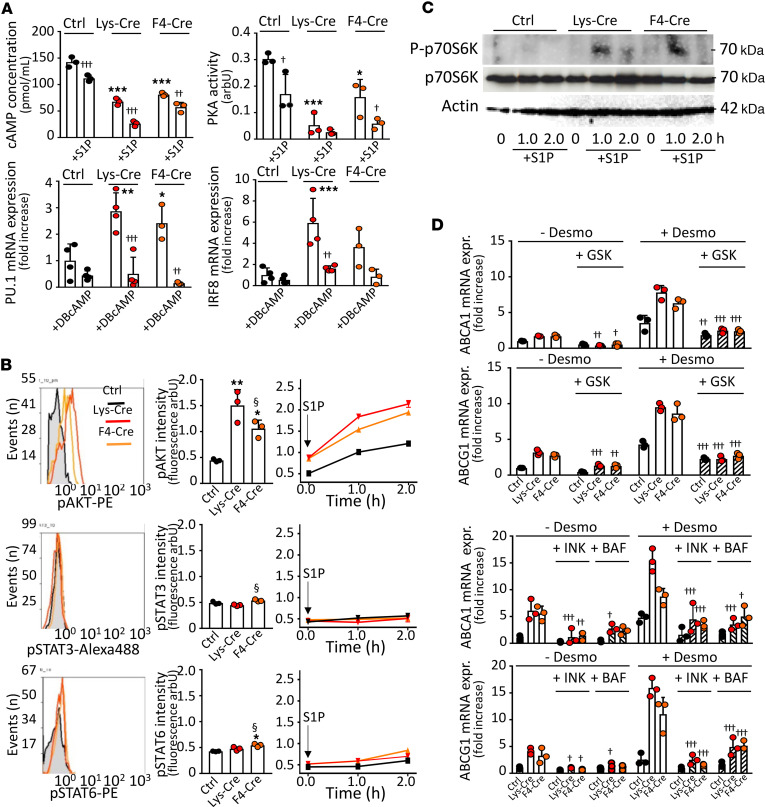
Figure 6. Stimulatory effects of S1P1 overexpression are mediated by PKA and AKT.
PMs from S1pr1-KI (Ctrl, n = 3–4), S1pr1-LysMCre (Lys-Cre, n = 3–4), or S1pr1-F4/80Cre (F4-Cre, n = 3–4) mice on ND were established in culture. (A) Cells were exposed to S1P (1.0 μmol/L) for 2 hours (upper panels) or dibutyryl-cAMP (DBcAMP) (0.25 mmol/L) for 24 hours (lower panels). cAMP levels and PKA activity were measured using enzyme immunoassay or Pep-Tag assay. Pu1 and Irf8 expressions were analyzed by qPCR. (B and C) PMs were analyzed for kinase activities or exposed to S1P (1.0 μmol/L) for indicated times. Intracellular stainings for phospho-AKT, phospho-STAT3, and phospho-STAT6 analyzed by flow cytometry (B). For mTOR1 activity, PMs lysates probed with antibodies against total and phosphorylated (P) p70S6 kinase (C). Blots representative for 2 independent experiments. (D) Cells were exposed for 30 minutes to GSK690693 (10.0 μmol/L), INK128 (0.2 μmol/L), or bafilomycin (1.0 μmol/L) prior to incubation with desmosterol (50 μmol/L) for 24 hours. Abca1 and Abcg1 genes analyzed by qPCR. Shown are results from 3 independent experiments. † - P < 0.05, †† - P < 0.01, ††† - P < 0.001 with vs. without treatment with activator/inhibitor, * - P < 0.05, ** - P < 0.01, *** - P < 0.001 (Lys-Cre vs. Ctrl or F4-Cre vs. Ctrl), § - P < 0.05 (Lys-Cre vs. F4-Cre, 1-way or 2-way ANOVA).