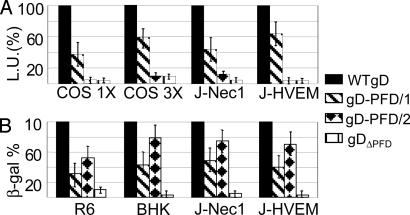
Fig. 3.
Cell-cell fusion and infectivity complementation of chimeric gD proteins. (A) Luciferase-based cell-cell fusion assay. Effector COS cells were transfected with plasmids for gH, gL, gB, chimeric, or WT-gD and T7 polymerase at 125 or 375 ng of each plasmid, corresponding to 1× and 3× amounts, respectively. Target cells [COS, J-nectin 1 (J-Nec1), and J-HVEM] were transfected with T7-luciferase. The negative control lacked gD (data not shown). The luciferase activity was expressed as luciferase units (L.U.). (B) Infectivity complementation. COS cells were transfected with chimeric or WT-gD and infected 4 h later with a gD-/+ stock of FgDβ (3 plaque-forming units per cell). The negative control consisted of cells not transfected with gD. Progeny virus was titrated at 24 h in gD-expressing cells (R6) or was quantified as β-galactosidase in baby hamster kidney, J-nec1, or J-HVEM cells. Details are as in the legend to Fig. 2.