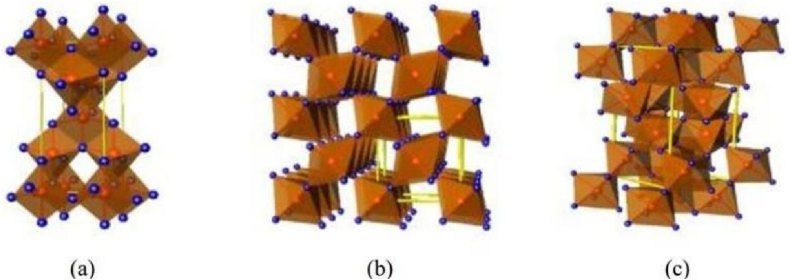
Fig. 1.
Crystalline structures of (a) anatase, (b) rutile, and (c) brookite. Red spheres represent Ti⁴⁺ ions, and blue spheres represent O2⁻ ions. Yellow lines denote unit cells, showing the different crystal structures: anatase's open tetragonal structure with efficient electron pathways, rutile's dense tetragonal configuration, and brookite's complex orthorhombic arrangement, contributing to the variations in photocatalytic properties.