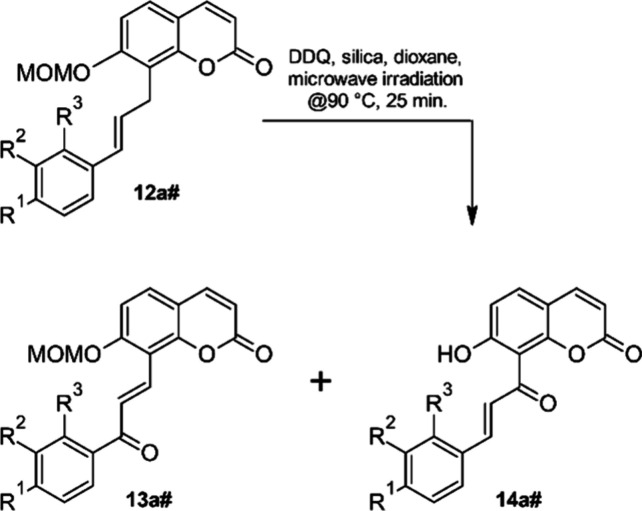
Table 4. Allylic Oxidation of 12a#: Scope and Limitations.
| entry | 12 | R1 | R2 | R3 | Product | yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12aa | H | H | H | 13aa | 56 |
| 2 | 12ab | F | H | H | 13ab | 85 |
| 3 | 12ac | Cl | H | H | 13ac | 47 |
| 4 | 12ad | Br | H | H | 13ad | 43 |
| 5 | 12ae | I | H | H | 13ae | 29a |
| 6 | 12af | OCH3 | H | H | 13af | 78a |
| 7 | 12ag | OH | H | H | 13ag | <5b |
| 8 | 12ah | CH3 | H | H | 13ah | n.d.c |
| 9 | 12ai | CO2Et | H | H | 13ai | 36 |
| 10 | 12ak | CF3 | H | H | 13ak | 22 |
| 11 | 12al | H | F | H | 13al | 33 |
| 12 | 12am | H | Cl | H | 13am | 60 |
| 13 | 12an | H | Br | H | 14an | 26 |
| 14 | 12ao | H | I | H | 13ao | n.d.c |
| 15 | 12ap | H | OCH3 | H | 13ap | 24 |
| 16 | 12aq | H | CH3 | H | 13aq | 37 |
| 17 | 12ar | H | CO2CH3 | H | 14ar | 48 |
| 18 | 12at | H | H | OCH3 | 13at | 56 |
| 19 | 12au | H | H | CO2CH3 | 14au | 92 |
Unprotected phenols 14ae (16%) and 14af (ca. 10%) were isolated as byproducts.
Decomposition of starting material.
n.d.: not determined; oxidation products 13 were detected by NMR but could not be isolated in pure form due to inseparable byproducts.