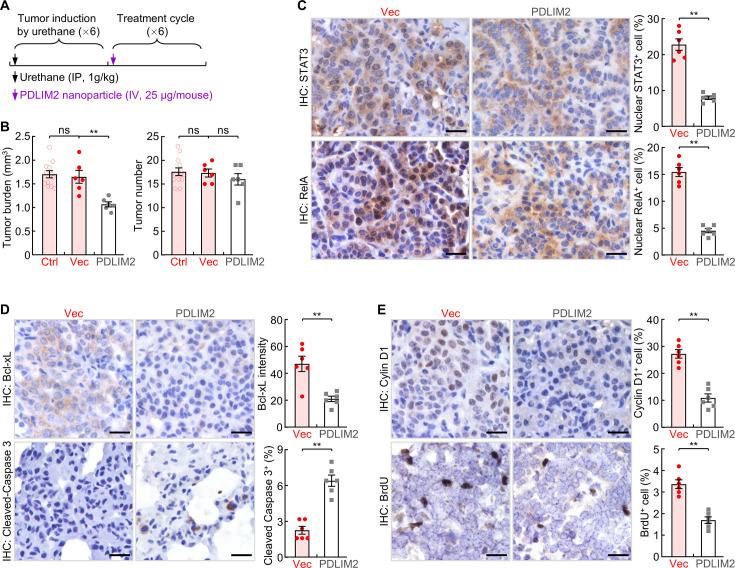
Figure 2. Systemic administration of PDLIM2 plasmid nanoparticles shows efficacy in mouse model of refractory lung cancer.
(A) Schedule of lung cancer induction and treatment. (B) Urethane model showing efficacy of intravenous administration of PDLIM2-expression plasmid nanoparticles for refractory lung cancer (n≥6). Nanoparticles with an empty vector plasmid (Vec) that was employed to express PDLIM2 were used as a control. (C) IHC staining showing decreased nuclear expression of STAT3 and RelA in lung tumors by PDLIM2 nanotherapy (n=6). (D) IHC staining showing decreased Bcl-xL and increased apoptosis marker cleaved caspase –3 in lung tumors by PDLIM2 nanotherapy (n=6). (E) IHC staining showing decreased Cyclin D1 and proliferation (BrdU incorporation) in lung tumors by PDLIM2 nanotherapy (n=6). Scale bar in (C–E), 20 μm. Student’s t test was performed (two tailed, unpaired) and data represent means ± SEM in (B–E). **p<0.01; ns, not statistically significant.