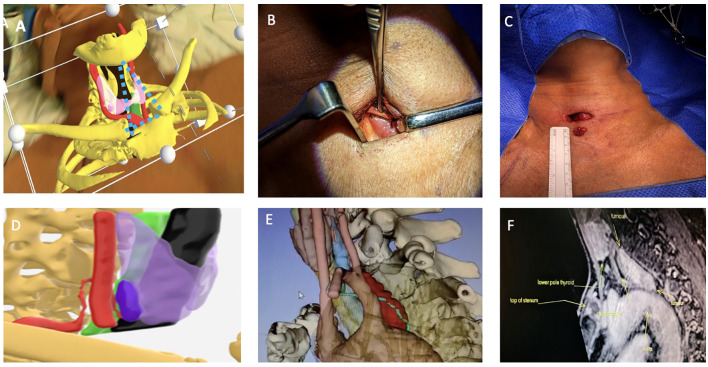
Figure 3.
Top row (A) Surgeon’s view from the right side of the operating table of 3D model superimposition on patient’s neck using Microsoft HoloLens2,the parathyroid adenoma (Right lower pink structure), thyroid (light purple in transparency), carotid artery (red) and bones (yellow), imaginary triangulation dotted lines in blue. (B) Shows incision placement and immediate location of the parathyroid adenoma with minimal dissection and no subplatysmal flap elevation. (C) Postoperative excision with maintained wound length as there was no need for excessive retraction. Bottom row (D) It shows side-view of the 3D model where ITA and its branch which supplies the parathyroid adenoma are reconstructed, in this model, thyroid gland (light purple), right parathyroid adenoma (deep purple), trachea (black) and carotid artery (red). (E) shows a very large parathyroid tumour in the prevertebral space closely related to the aortic arch and the thoracic duct (lime green). (F) MRI sagittal view shows relation of parathyroid adenoma to aortic arch but thoracic duct was more difficult to visualise. The thoracic duct was identified and ligated at the start of the dissection to avoid a thoracic duct injury and a chyle leak.