Fig. 9.
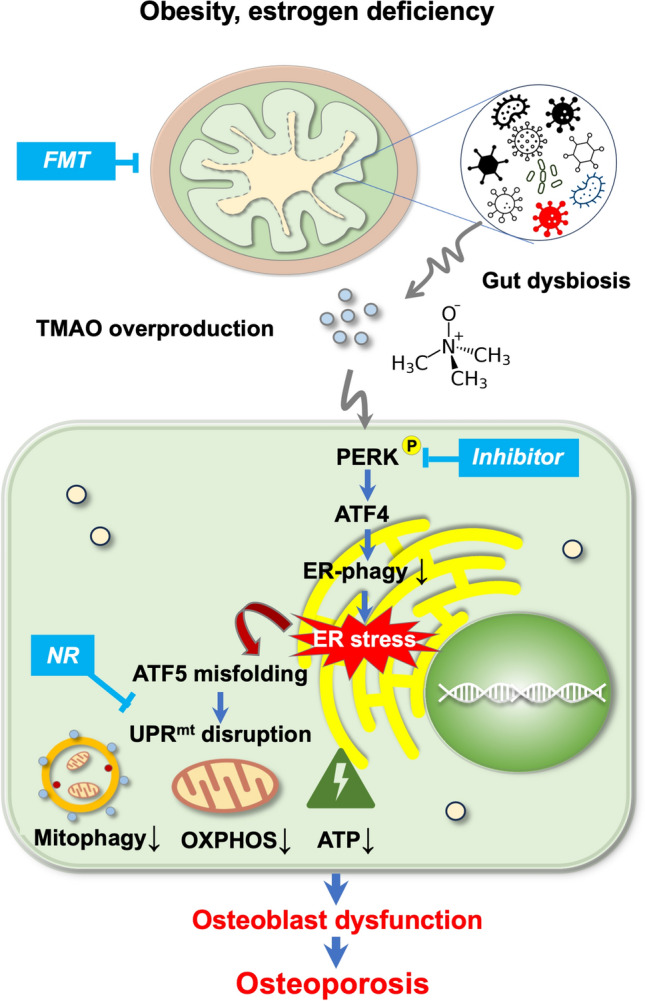
Hypothetical model of how gut microbiota-derived TMAO changes bone integrity. Gut microorganism dysbiosis elevates TMAO production in obese or ovariectomized mice. This metabolite then activates PERK and ATF4 to suppress ER autophagy and thus elevating ER stress, which leads to mitochondrial ATF5 misfolding and UPRmt disruption, together with decreased mitophagy, OXPHOS, and ATP synthesis. This consequently accelerates osteoblast dysfunction, leading to bone loss. FMT (from healthy donors), PERK inhibitor or UPRmt activator mitigates TMAO-induced loss of osteoblastic activity loss and bone mass. FMT, fecal microbiota transplantation; TMAO, trimethylamine-n-oxide; PERK, protein kinase R-link endoplasmic reticulum kinase; ATF4, activating transcription factor 4; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ATF5, activating transcription factor 5; NR, nicotinamide ribose; UPRmt, mitochondrial unfolding protein response; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation
