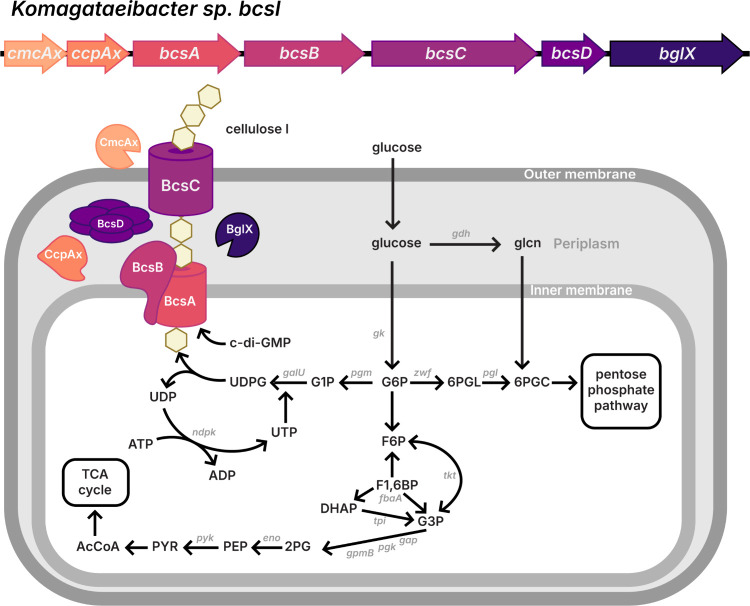
Figure 2.
Overview of BC synthesis in Komagataeibacter spp. Relevant bcs cellulose synthase operon genes bcsABCD and the accessory genes cmcAx, ccpA, and bglX, and their respective proteins are highlighted in color. The complete bcsI (type I) operon is shown here for simplicity, though several other copies of the bcs operon, typically modified, exist throughout the Komagataeibacter species chromosome. Cellulose is synthesized from glucose, which is converted into UDP-glucose before being added onto to the reducing end of the glucan chain (shown as yellow hexagons) at the inner membrane and then exported out of the bacterial cell. Various modifications to the cellulose chain occur in the periplasm and extracellularly. Enzyme abbreviations from top to bottom: gdh (glucose dehydrogenase), gk (glucose kinase), galU (UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase), pgm (phosphoglucomutase), zwf (glucose 6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase), pgl (6-phosphogluconolactonase), ndpk (nucleoside diphosphate kinase), tkt (transketolase), fbaA (fructose bisphosphate adolase A), tpi (triosephosphate isomerase), pyk (pyruvate kinase), eno (enolase), gpmB (2,3-bisphosphoglycerate-independent phosphoglycerate mutase B), pgk (phosphoglycerate kinase), and gap (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase). Metabolite abbreviations from top to bottom: glcn (gluconate), c-di-GMP (cyclic diguanylate), UDP (uridine diphosphate), UDPG (uridine diphosphate glucose), G1P (glucose 1-phosphate), G6P (glucose 6-phosphate), 6PGL (6-phosphogluconolactone), 6PGC (6-phosphogluconate), ATP (adenosine triphosphate), ADP (adenosine diphosphate), UTP (uridine triphosphate), F6P (fructose 6-phosphate), F1,6BP (fructose-1,6-diphosphate), DHAP (dihydroxyacetone phosphate), G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate), AcCoA (acetyl coenzyme A), PYR (pyruvate), PEP (phosphoenol pyruvate), and 2PG (2-phosphoglyceric acid).